Usage and Adherence of Seven Advanced Therapies with Differing Mechanisms of Action for Inflammatory Arthritis in Canada
- PMID: 36045308
- PMCID: PMC9510085
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-022-00485-2
Usage and Adherence of Seven Advanced Therapies with Differing Mechanisms of Action for Inflammatory Arthritis in Canada
Abstract
Introduction: This retrospective, observational study aimed to analyze and assess adherence, persistence, dosing, and use of concomitant medications of seven self-administered target drugs (abatacept, golimumab, secukinumab, tocilizumab, ustekinumab, apremilast, and tofacitinib) that are currently available in Canada for the treatment of inflammatory arthritis (IA).
Methods: We used IQVIA's longitudinal claims databases, which include private drug plans and public plans. Patients with IA identified using a proprietary indication algorithm who initiated treatment with any of the target drugs between January 2015 and February 2019 were selected and followed for 12 months.
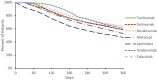
Results: Golimumab and apremilast had the highest proportion of patients (~ 75%) who were bio-naïve and secukinumab had the fewest bio-naïve patients (~ 43%). The oral therapies, apremilast and tofacitinib, had the lowest percentage of adherent patients (73% and 71%) followed by abatacept (83%), while the remaining drugs had adherence around 90%. Secukinumab and tofacitinib had the highest 12-month persistence rate (63% and 61%), while abatacept and apremilast had the lowest persistence rate (52% and 47%). Oral corticosteroid (OCS) use was not significantly associated with adherence. Tocilizumab, secukinumab, and ustekinumab had the highest proportion of patients (> 20%) with dose escalation at 3-4 months from index. OCS and conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (cDMARD) use decreased in post-index period across all target drugs.
Conclusion: This study identified substantial differences in patient baseline characteristics. Patients on injectable biologics were more likely to be adherent compared with those on oral drugs, possibly owing to longer dosing intervals. Other outcomes at 12 months appeared similar as evidenced by tapering of concomitant medications, although differences in persistence and dose escalation were noted.
Keywords: Adherence; Administrative data; Inflammatory arthritis; Persistence.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative effectiveness of abatacept, apremilast, secukinumab and ustekinumab treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Rheumatol Int. 2018 Feb;38(2):189-201. doi: 10.1007/s00296-017-3919-7. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Rheumatol Int. 2018. PMID: 29285605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Real-World Experience of Tofacitinib for Psoriatic Arthritis: Data from a United States Healthcare Claims Database.Adv Ther. 2022 Jun;39(6):2932-2945. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02084-7. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35482248 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of targeted DMARDs for active psoriatic arthritis during induction therapy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Dec;49(3):381-388. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.06.001. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019. PMID: 31272807
-
Treatment Switch Patterns and Healthcare Costs in Biologic-Naive Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis.Adv Ther. 2020 May;37(5):2098-2115. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01262-9. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 32141018 Free PMC article.
-
Adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, tocilizumab and abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis not previously treated with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and after the failure of conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs only: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2016 Apr;20(35):1-610. doi: 10.3310/hta20350. Health Technol Assess. 2016. PMID: 27140438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Canadian Chronic Disease Surveillance System (CCDSS). https://health-infobase.canada.ca/ccdss/data-tool/. Accessed 20 July 2020.
-
- Salaffi F, Di Carlo M, Carotti M, Farah S, Ciapetti A, Gutierrez M. The impact of different rheumatic diseases on health-related quality of life: a comparison with a selected sample of healthy individuals using SF-36 questionnaire, EQ-5D and SF-6D utility values. Acta Biomed. 2019;89(4):541–557. doi: 10.23750/abm.v89i4.7298. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources