Structural basis for activation of Arf1 at the Golgi complex
- PMID: 36044848
- PMCID: PMC9469209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111282
Structural basis for activation of Arf1 at the Golgi complex
Abstract
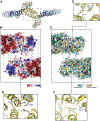
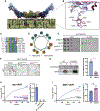
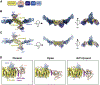
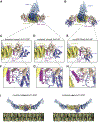
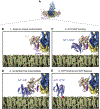
The Golgi complex is the central sorting station of the eukaryotic secretory pathway. Traffic through the Golgi requires activation of Arf guanosine triphosphatases that orchestrate cargo sorting and vesicle formation by recruiting an array of effector proteins. Arf activation and Golgi membrane association is controlled by large guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) possessing multiple conserved regulatory domains. Here we present cryoelectron microscopy (cryoEM) structures of full-length Gea2, the yeast paralog of the human Arf-GEF GBF1, that reveal the organization of these regulatory domains and explain how Gea2 binds to the Golgi membrane surface. We find that the GEF domain adopts two different conformations compatible with different stages of the Arf activation reaction. The structure of a Gea2-Arf1 activation intermediate suggests that the movement of the GEF domain primes Arf1 for membrane insertion upon guanosine triphosphate binding. We propose that conformational switching of Gea2 during the nucleotide exchange reaction promotes membrane insertion of Arf1.
Keywords: ARF1; CP: Cell biology; GTPase; Golgi; cryoEM; membrane; membrane insertion.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
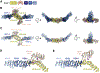
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Arf activation occurs via distinct mechanisms at early and late Golgi compartments.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Dec 1;28(25):3660-3671. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-06-0370. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28978742 Free PMC article.
-
The p24 Complex Contributes to Specify Arf1 for COPI Coat Selection.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 3;22(1):423. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010423. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33401608 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Insights into Arl1-Mediated Targeting of the Arf-GEF BIG1 to the trans-Golgi.Cell Rep. 2016 Jul 19;16(3):839-50. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.06.022. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27373159 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple activities for Arf1 at the Golgi complex.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Jul 10;1744(3):364-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.03.001. Epub 2005 Mar 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 15979507 Review.
-
The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and SAR1 in vesicular trafficking in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 1;1664(1):9-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.04.005. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15238254 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for Rab6 activation by the Ric1-Rgp1 complex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 6:2024.05.06.592747. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.06.592747. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 4;15(1):10561. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54869-9 PMID: 38766083 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The Arf-GAP Age2 localizes to the late-Golgi via a conserved amphipathic helix.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 24:2023.07.23.550229. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.23.550229. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Nov 1;34(12):ar119. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-07-0283 PMID: 37546741 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The Arf-GAP Age2 localizes to the late-Golgi via a conserved amphipathic helix.Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Nov 1;34(12):ar119. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-07-0283. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2023. PMID: 37672345 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into an Arl1-ArfGEF complex involved in Golgi recruitment of a GRIP-domain golgin.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 2;15(1):1942. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46304-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38431634 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of Arf1 inactivation regulates Golgi organisation and function in non-adherent fibroblasts.Biol Open. 2023 Apr 15;12(4):bio059669. doi: 10.1242/bio.059669. Epub 2023 May 4. Biol Open. 2023. PMID: 36946871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amor JC, Harrison DH, Kahn RA, and Ringe D (1994). Structure of the human ADP-ribosylation factor 1 complexed with GDP. Nature 372, 704–708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

