Chondroitin polymerizing factor predicts a poor prognosis and promotes breast cancer progression via the upstream TGF-β1/SMAD3 and JNK axis activation
- PMID: 36042157
- PMCID: PMC10030767
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-022-00684-0
Chondroitin polymerizing factor predicts a poor prognosis and promotes breast cancer progression via the upstream TGF-β1/SMAD3 and JNK axis activation
Abstract
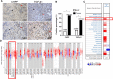
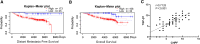
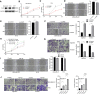
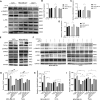
Aberrant composition of glycans in the tumor microenvironment (TME) contributes to tumor progression and metastasis. Chondroitin polymerizing factor (CHPF) is a glycosyltransferase that catalyzes the biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate (CS). It is also correlated to transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) expression, a crucial mediator in the interaction of cancer cells with TME. In this study, we investigated the association of CHPF expression with the clinicopathological features of breast cancer (BRCA), as well the oncogenic effect and the underling mechanisms of CHPF upon BRCA cells. We found that CHPF expression is significantly increased in human BRCA tissues, and it is positively associated with TGF-β expression (r = 0.7125). The high-expression of CHPF predicts a poor prognosis and is positively correlated with tumor mass, lymph node metastasis, clinical staging and HER-2 negative-expression. The mechanistic study revealed that it promotes BRCA cell proliferation, migration and invasion through TGF-β1-induced SMAD3 and JNK activation in vitro, JNK (SP600125) or SMAD3 (SIS3) inhibitor can remove the promotion of CHPF upon cell proliferation, migration and invasion in MDA-MB-231 cells, which is derived from triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Collectively, our finding suggested CHPF may function as an oncogene and is highly expressed in human BRCA tissues. Pharmacological blockade of the upstream of JNK or SMAD3 signaling may provide a novel therapeutic target for refractory TNBC patients with CHPF abnormal high-expression.
Keywords: CHPF; Human breast cancer; JNK signaling; MDA-MB-231 cell line; SMAD3 signaling; TGF-β1.
© 2022. The International CCN Society.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TGF-β Stimulates Expression of Chondroitin Polymerizing Factor in Nucleus Pulposus Cells Through the Smad3, RhoA/ROCK1, and MAPK Signaling Pathways.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Jan;119(1):566-579. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26215. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 28608941
-
CHPF Regulates the Aggressive Phenotypes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via the Modulation of the Decorin and TGF-β Pathways.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 12;13(6):1261. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061261. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809195 Free PMC article.
-
Chondroitin polymerizing factor promotes breast carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and migration and affects expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related markers.FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Feb;11(2):423-434. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13062. Epub 2021 Jan 7. FEBS Open Bio. 2021. PMID: 33301643 Free PMC article.
-
Smad3 phosphoisoform-mediated signaling during sporadic human colorectal carcinogenesis.Histol Histopathol. 2006 Jun;21(6):645-62. doi: 10.14670/HH-21.645. Histol Histopathol. 2006. PMID: 16528675 Review.
-
The Role of the Tumor Microenvironment in Triple-Positive Breast Cancer Progression and Therapeutic Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 20;15(22):5493. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225493. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of NDUFAF6 on breast cancer prognosis: linking mitochondrial regulation to immune response and PD-L1 expression.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Mar 8;24(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03244-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38459583 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting chondroitin sulfate suppresses macropinocytosis of breast cancer cells by modulating syndecan-1 expression.Mol Oncol. 2024 Oct;18(10):2569-2585. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13667. Epub 2024 May 21. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38770553 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

