Impact of NSCLC metabolic remodeling on immunotherapy effectiveness
- PMID: 36038935
- PMCID: PMC9425942
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-022-00412-1
Impact of NSCLC metabolic remodeling on immunotherapy effectiveness
Abstract
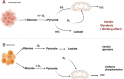
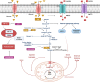
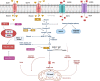
It is known that metabolic reprogramming (MR) contributes to tumorigenesis through the activation of processes that support survival of cells, proliferation, and grow in the tumor microenvironment. In order to keep the tumor proliferating at a high rate, metabolic pathways must be upregulated, and tumor metabolism must be adapted to meet this requirement. Additionally, immune cells engage in metabolic remodeling to maintain body and self-health. With the advent of immunotherapy, the fate of individuals suffering from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been transformed dramatically. MR may have a profound influence on their prognosis. The aim of this review is to summarize current research advancements in metabolic reprogramming and their impact on immunotherapy in NSCLC. Moreover, we talk about promising approaches targeting and manipulating metabolic pathways to improve cancer immunotherapy's effectiveness in NSCLC.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Metabolic reprogramming; NSCLC; TME.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Bladder Cancer Metabolic Reprogramming in the Effectiveness of Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 14;13(2):288. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020288. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33466735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Estrogen on the NSCLC Microenvironment: A Comprehensive Picture and Clinical Implications.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 18;10:137. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00137. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32133288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of metabolic reprogramming in tumor immune evasion and immunotherapy.Sci China Life Sci. 2021 Apr;64(4):534-547. doi: 10.1007/s11427-019-1735-4. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Sci China Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32815067 Review.
-
VEGF/VEGFR-Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 May 29;18(9):3845-3858. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.70958. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35813484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming Induces Immune Cell Dysfunction in the Tumor Microenvironment of Multiple Myeloma.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 15;10:591342. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.591342. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33520703 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pan-cancer analysis of super enhancer-induced PRR7-AS1 as a potential prognostic and immunological biomarker.Front Genet. 2023 Apr 6;14:1160599. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1160599. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37091809 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Cell-Intrinsic Alterations Associated with an Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment and Resistance to Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;15(12):3076. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123076. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy metabolism as the hub of advanced non-small cell lung cancer management: a comprehensive view in the framework of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine.EPMA J. 2024 Apr 8;15(2):289-319. doi: 10.1007/s13167-024-00357-5. eCollection 2024 Jun. EPMA J. 2024. PMID: 38841622 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

