Time Domains of Hypoxia Responses and -Omics Insights
- PMID: 36035495
- PMCID: PMC9400701
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.885295
Time Domains of Hypoxia Responses and -Omics Insights
Abstract
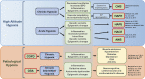
The ability to respond rapidly to changes in oxygen tension is critical for many forms of life. Challenges to oxygen homeostasis, specifically in the contexts of evolutionary biology and biomedicine, provide important insights into mechanisms of hypoxia adaptation and tolerance. Here we synthesize findings across varying time domains of hypoxia in terms of oxygen delivery, ranging from early animal to modern human evolution and examine the potential impacts of environmental and clinical challenges through emerging multi-omics approaches. We discuss how diverse animal species have adapted to hypoxic environments, how humans vary in their responses to hypoxia (i.e., in the context of high-altitude exposure, cardiopulmonary disease, and sleep apnea), and how findings from each of these fields inform the other and lead to promising new directions in basic and clinical hypoxia research.
Keywords: adaptation; high altitude; hypoxia; integrative physiology; oxygen.
Copyright © 2022 Yu, Non, Heinrich, Gu, Alcock, Moya, Lawrence, Tift, O'Brien, Storz, Signore, Khudyakov, Milsom, Wilson, Beall, Villafuerte, Stobdan, Julian, Moore, Fuster, Stokes, Milner, West, Zhang, Shyy, Childebayeva, Vázquez-Medina, Pham, Mesarwi, Hall, Cheviron, Sieker, Blood, Yuan, Scott, Rana, Ponganis, Malhotra, Powell and Simonson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[A Review of High-altitude Hypoxia Adaptation and Hypoxic Solid Tumor].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 Jan;52(1):50-56. doi: 10.12182/20210160504. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 33474889 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Genetic adaptation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway to oxygen pressure among eurasian human populations.Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Nov;29(11):3359-70. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss144. Epub 2012 May 23. Mol Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 22628534
-
Coordinated changes across the O2 transport pathway underlie adaptive increases in thermogenic capacity in high-altitude deer mice.Proc Biol Sci. 2020 May 27;287(1927):20192750. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.2750. Epub 2020 May 20. Proc Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32429808 Free PMC article.
-
What to do with low O2: Redox adaptations in vertebrates native to hypoxic environments.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2022 Sep;271:111259. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.111259. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35724954 Review.
-
Lungs at high-altitude: genomic insights into hypoxic responses.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Jul 1;119(1):1-15. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00513.2014. Epub 2015 Apr 24. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 25911686 Review.
Cited by
-
EPAS1/HIF-2α: a key regulator for chronic hypoxia across species.J Physiol. 2022 Sep;600(18):4053-4054. doi: 10.1113/JP283554. Epub 2022 Aug 21. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35932457 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Understanding human aging and the fundamental cell signaling link in age-related diseases: the middle-aging hypovascularity hypoxia hypothesis.Front Aging. 2023 Jun 13;4:1196648. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2023.1196648. eCollection 2023. Front Aging. 2023. PMID: 37384143 Free PMC article.
-
Consistent differences in brain structure and functional connectivity in high-altitude native Tibetans and immigrants.Brain Imaging Behav. 2023 Jun;17(3):271-281. doi: 10.1007/s11682-023-00759-5. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023. PMID: 36694086
-
Manipulative neuroparasites: uncovering the intricacies of neurological host control.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Aug 21;205(9):314. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03637-2. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37603130 Review.
-
Functional EPAS1/HIF2A missense variant is associated with hematocrit in Andean highlanders.Sci Adv. 2024 Feb 9;10(6):eadj5661. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj5661. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38335297 Free PMC article.

