Fibroblasts in intestinal homeostasis, damage, and repair
- PMID: 36032088
- PMCID: PMC9399414
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.924866
Fibroblasts in intestinal homeostasis, damage, and repair
Abstract
The mammalian intestine is a self-renewing tissue that ensures nutrient absorption while acting as a barrier against environmental insults. This is achieved by mature intestinal epithelial cells, the renewing capacity of intestinal stem cells at the base of the crypts, the development of immune tolerance, and the regulatory functions of stromal cells. Upon intestinal injury or inflammation, this tightly regulated mucosal homeostasis is disrupted and is followed by a series of events that lead to tissue repair and the restoration of organ function. It is now well established that fibroblasts play significant roles both in the maintenance of epithelial and immune homeostasis in the intestine and the response to tissue damage mainly through the secretion of a variety of soluble mediators and ligands and the remodeling of the extracellular matrix. In addition, recent advances in single-cell transcriptomics have revealed an unexpected heterogeneity of fibroblasts that comprise distinct cell subsets in normal and inflammatory conditions, indicative of diverse functions. However, there is still little consensus on the number, terminology, and functional properties of these subsets. Moreover, it is still unclear how individual fibroblast subsets can regulate intestinal repair processes and what is their impact on the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. In this mini-review, we aim to provide a concise overview of recent advances in the field, that we believe will help clarify current concepts on fibroblast heterogeneity and functions and advance our understanding of the contribution of fibroblasts in intestinal damage and repair.
Keywords: epithelial homeostasis; heterogeneity; immune responses; mesenchymal cells; regeneration; tissue injury.
Copyright © 2022 Chalkidi, Paraskeva and Koliaraki.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
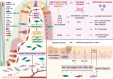
Similar articles
-
Immune niches orchestrated by intestinal mesenchymal stromal cells lining the crypt-villus.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 3;13:1057932. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1057932. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal Stromal Cells in the Turmoil of Inflammation and Defective Connective Tissue Remodeling in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024 Sep 3;30(9):1604-1618. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izae066. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024. PMID: 38581412 Review.
-
Tissue Niches Formed by Intestinal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Mucosal Homeostasis and Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 6;23(9):5181. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095181. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune cell-derived signals governing epithelial phenotypes in homeostasis and inflammation.Trends Mol Med. 2024 Mar;30(3):239-251. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2024.01.001. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Trends Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38320941 Review.
-
Heterogeneity of ILC2s in the Intestine; Homeostasis and Pathology.Front Immunol. 2022 May 30;13:867351. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867351. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35707544 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Landscape of Interactions between Stromal and Myeloid Cells in Ileal Crohn's Disease; Indications of an Important Role for Fibroblast-Derived CCL-2.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 26;12(8):1674. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081674. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200138 Free PMC article.
-
Current understanding of the interplay between extracellular matrix remodelling and gut permeability in health and disease.Cell Death Discov. 2024 May 27;10(1):258. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02015-1. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38802341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterizing the human intestinal chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan sulfation signature in inflammatory bowel disease.Sci Rep. 2024 May 23;14(1):11839. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60959-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38782973 Free PMC article.
-
Subepithelial Stromal Cells: Their Roles and Interactions with Intestinal Epithelial Cells during Gut Mucosal Homeostasis and Regeneration.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 17;12(3):668. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030668. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic arsenic exposure affects stromal cells and signaling in the small intestine in a sex-specific manner.Toxicol Sci. 2024 Mar 26;198(2):303-315. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae016. Toxicol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38310360
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

