Impact of dyslipidemia on the cumulative pregnancy outcomes after first ovarian stimulation
- PMID: 36017313
- PMCID: PMC9395644
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.915424
Impact of dyslipidemia on the cumulative pregnancy outcomes after first ovarian stimulation
Abstract
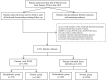
Objectives: To investigate the cumulative live birth rate (CLBR) according to lipid metabolism in patients with or without polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) undergoing their first complete in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI) cycles.
Patients: A total of 1,470 patients with PCOS and 3,232 patients without PCOS who underwent their first complete IVF/ICSI cycles from January 2016 to June 2018 were included. During a minimum of 2 years of follow-up, they had achieved at least one live birth or used all available embryos. The cumulative pregnancy outcomes were compared based on the patients' blood lipid parameters, including triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), in the two populations. Patients with an abnormal level of one or more of these four indicators were considered the dyslipidemia group. Patients whose four indicators were normal were considered the control group.
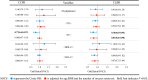
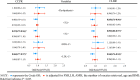
Results: Among 1,470 patients with PCOS, the cumulative pregnancy outcomes were similar in the dyslipidemia group and control group. Logistic regression analysis showed that the TC levels were significantly negatively associated with the cumulative live birth rate (CLBR) after adjustment for confounding factors such as age and BMI (aOR 0.81, 95% CI 0.66-0.98, P<0.05). Among the 3,232 patients without PCOS, there was no significant difference in the cumulative pregnancy outcomes between the dyslipidemia group and the control group. No significant correlations were found in other logistic regression analyses.
Conclusions: TC negatively impacts the CLBR after first ovarian stimulation in PCOS patients. PCOS patients with dyslipidemia caused by elevated TC may have a poor CLBR.
Keywords: assisted reproductive technology; cumulative live birth rate; dyslipidemia; lipid metabolism; polycystic ovary syndrome.
Copyright © 2022 Jiang, Lu, Cai, Liu and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that the study was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be interpreted as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effects of dyslipidemia on IVF/ICSI pregnancy outcome in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 25;53(6):402-408. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567x.2018.06.008. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29961283 Chinese.
-
Factors affecting cumulative live birth rate after the 1st oocyte retrieved in polycystic ovary syndrome patients in women during IVF/ICSI-ET.J Ovarian Res. 2023 Oct 13;16(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01290-3. J Ovarian Res. 2023. PMID: 37833722 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Cumulative Live Birth Rate Between Aged PCOS Women and Controls in IVF/ICSI Cycles.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Sep 28;12:724333. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.724333. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34650517 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin treatment before and during IVF or ICSI in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Apr 15;(2):CD006105. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006105.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Nov 18;(11):CD006105. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006105.pub3 PMID: 19370625 Updated. Review.
-
Effects of metformin in women with polycystic ovary syndrome treated with gonadotrophins for in vitro fertilisation and intracytoplasmic sperm injection cycles: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.BJOG. 2013 Feb;120(3):267-76. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.12070. Epub 2012 Nov 30. BJOG. 2013. PMID: 23194199 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the gut microbiota in polycystic ovary syndrome with dyslipidemia.BMC Microbiol. 2024 May 17;24(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03329-x. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38760705 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoprotein alterations in endocrine disorders - a review of the recent developments in the field.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 2;15:1354098. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1354098. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38628593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of high-normal fasting blood glucose on ART outcomes of frozen-thawed single blastocyst transfer in women with normal BMI.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024 Oct;41(10):2615-2623. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03191-w. Epub 2024 Jul 6. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2024. PMID: 38970737
-
Adiposity and lipid metabolism indicators mediate the adverse effect of glucose metabolism indicators on oogenesis and embryogenesis in PCOS women undergoing IVF/ICSI cycles.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Jul 3;28(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01174-8. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37400924 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperlipidemia is negatively associated with pregnancy outcomes in patients following frozen-thawed embryo transfer: A retrospective study.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 4;7(3):e1947. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1947. eCollection 2024 Mar. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38440261 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

