Association of lncRNA LINC01173 Expression with Vitamin-D and Vitamin B12 Level Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- PMID: 36016630
- PMCID: PMC9397532
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S369012
Association of lncRNA LINC01173 Expression with Vitamin-D and Vitamin B12 Level Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Abstract
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has risen to become the world's most serious public health problem in recent years, and the role of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the onset and progression of T2DM, as well as special attention to vitamins, has gotten a lot of attention recently.
Methods: The aim of the study was to analyze lncRNA LINC01173 expression along with assessment of vitamin-D and B12 among the T2DM cases. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to analyze the expression of lncRNA LINC01173. Vitamin-D and B12 were analyzed by chemiluminescence-based assay.
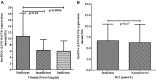
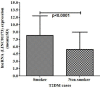
Results: The present study observed that the T2DM cases had 6.67-fold increased lncRNA LINC01173 expression compared to healthy controls. Expression of lncRNA LINC01173 was found to be associated with hypertension (p=0.03), wound healing (p=0.04), and blurred vision (p<0.0001). It was observed that the T2DM cases with vitamin-D deficiency had a significant association with fasting glucose level (p=0.01) and HbA1C level (p=0.01) among the T2DM cases. The association of lncRNA LINC01173 with vitamin-D was analyzed and it was observed that the vitamin-D deficient cases had higher lncRNA LINC01173 expression compared to insufficient T2DM cases (p=0.01) and sufficient T2DM cases (p=0.0006). It was also observed that the T2DM cases with smoking had a 8.33-fold lncRNA LINC01173 expression while non-smokers had a 5.43-fold lncRNA LINC01173 expression (p<0.0001).
Conclusion: The study concluded that the increased lncRNA LINC01173 expression was observed to be linked with alteration in vitamin-D level and smoking habit. Altered expression of lncRNA LINC01173 expression was linked with fasting glucose and HbA1C alteration. Collectively, lncRNA LINC01173 expression, vitamin-D alteration, as well as smoking habit may cause the disease severity and increase the pathogenesis of disease.
Keywords: diabetes; long noncoding RNA; vitamin-B12; vitamin-D.
© 2022 Aladel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating long non-coding RNAs NKILA, NEAT1, MALAT1, and MIAT expression and their association in type 2 diabetes mellitus.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2021 Jan;9(1):e001821. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001821. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2021. Retraction in: BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2025 Jan 30;13(1):e001821.ret. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001821.ret PMID: 33436407 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Evaluation of miRNA-143 and miRNA-145 Expression and Their Association with Vitamin-D Status Among Obese and Non-Obese Type-2 Diabetic Patients.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2022 Dec 28;15:2979-2990. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S391996. eCollection 2022. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2022. PMID: 36597468 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Importance of FNDC-5 and Selectin-E mRNA Expression Among Type 2 Diabetics with and without Obesity.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022 Apr 2;15:1011-1021. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S352483. eCollection 2022. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022. PMID: 35401010 Free PMC article.
-
Study of relationship between total vitamin D level and NAFLD in a sample of Egyptian patients with and without T2DM.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019 May-Jun;13(3):1769-1771. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31235092 Review.
-
Shining the light on Sunshine: a systematic review of the influence of sun exposure on type 2 diabetes mellitus-related outcomes.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014 Dec;81(6):799-811. doi: 10.1111/cen.12567. Epub 2014 Sep 9. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014. PMID: 25066830 Review.
Cited by
-
Tracing vitamins on the long non-coding lane of the transcriptome: vitamin regulation of LncRNAs.Genes Nutr. 2024 Mar 12;19(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12263-024-00739-4. Genes Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38475720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th edn. Brussels, and Belgium, “IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th edn”; 2019. Available from: https://www.diabetesatlas.org. Accessed August 5, 2022.
-
- Ruan Y, Lin N, Ma Q, et al. Circulating LncRNAs analysis in cases with type 2 diabetes reveals novel genes influencing glucose metabolism and Islet β-cell function. CPB. 2018;46(1):335–350. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

