Promising Antimycobacterial Activities of Flavonoids against Mycobacterium sp. Drug Targets: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 36014572
- PMCID: PMC9415813
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27165335
Promising Antimycobacterial Activities of Flavonoids against Mycobacterium sp. Drug Targets: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
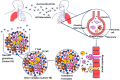
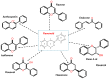
Tuberculosis (TB) caused by the bacterial pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) remains a threat to mankind, with over a billion of deaths in the last two centuries. Recent advancements in science have contributed to an understanding of Mtb pathogenesis and developed effective control tools, including effective drugs to control the global pandemic. However, the emergence of drug resistant Mtb strains has seriously affected the TB eradication program around the world. There is, therefore, an urgent need to develop new drugs for TB treatment, which has grown researchers' interest in small molecule-based drug designing and development. The small molecules-based treatments hold significant potential to overcome drug resistance and even provide opportunities for multimodal therapy. In this context, various natural and synthetic flavonoids were reported for the effective treatment of TB. In this review, we have summarized the recent advancement in the understanding of Mtb pathogenesis and the importance of both natural and synthetic flavonoids against Mtb infection studied using in vitro and in silico methods. We have also included flavonoids that are able to inhibit the growth of non-tubercular mycobacterial organisms. Hence, understanding the therapeutic properties of flavonoids can be useful for the future treatment of TB.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; anti-tubercular compounds; drug discovery; flavonoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
-
Editorial: Current status and perspective on drug targets in tubercle bacilli and drug design of antituberculous agents based on structure-activity relationship.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(27):4305-6. doi: 10.2174/1381612819666131118203915. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24245755
-
Recent updates on drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Appl Microbiol. 2020 Jun;128(6):1547-1567. doi: 10.1111/jam.14478. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31595643 Review.
-
[Prospects for development of new antituberculous drugs].Kekkaku. 2002 Aug;77(8):573-84. Kekkaku. 2002. PMID: 12235850 Japanese.
-
Host-directed therapy targeting the Mycobacterium tuberculosis granuloma: a review.Semin Immunopathol. 2016 Mar;38(2):167-83. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0537-x. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Semin Immunopathol. 2016. PMID: 26510950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antitubercular drugs: possible role of natural products acting as antituberculosis medication in overcoming drug resistance and drug-induced hepatotoxicity.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;397(3):1251-1273. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02679-z. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37665346 Review.
-
Antimycobacterial Activity of Hedeoma drummondii against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;12(5):833. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12050833. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37237736 Free PMC article.
-
Bioassay-guided isolation and structure elucidation of anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis compounds from Galatella grimmii (Regel & Schmalh.) Sennikov.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Oct 1;24(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04632-w. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39354550 Free PMC article.
-
Isoflavonoid and Furanochromone Natural Products as Potential DNA Gyrase Inhibitors: Computational, Spectral, and Antimycobacterial Studies.ACS Omega. 2023 Apr 28;8(18):16228-16240. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00684. eCollection 2023 May 9. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37179626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakaya J., Khan M., Ntoumi F., Aklillu E., Fatima R., Mwaba P., Kapata N., Mfinanga S., Hasnain S.E., Katoto P.D. Global Tuberculosis Report 2020–Reflections on the Global TB Burden, Treatment and Prevention Efforts. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021;113:S7–S12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical