Regulatory Role of Apoptotic and Inflammasome Related Proteins and Their Possible Functional Aspect in Thiram Associated Tibial Dyschondroplasia of Poultry
- PMID: 36009620
- PMCID: PMC9404426
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12162028
Regulatory Role of Apoptotic and Inflammasome Related Proteins and Their Possible Functional Aspect in Thiram Associated Tibial Dyschondroplasia of Poultry
Abstract
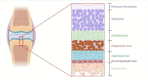
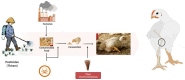
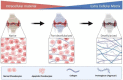
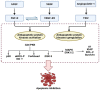
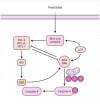
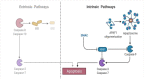
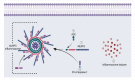
Tibial dyschondroplasia debilities apoptotic and inflammasomal conditions that can further destroy chondrocytes. Inflammasomes are specialized protein complexes that process pro-inflammatory cytokines, e.g., interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-18. Moreover, there is mounting evidence that many of the signaling molecules that govern programmed cell death also affect inflammasome activation in a cell-intrinsic way. During the last decade, apoptotic functions have been described for signaling molecules involving inflammatory responses and cell death pathways. Considering these exceptional developments in the knowledge of processes, this review gives a glimpse of the significance of these two pathways and their connected proteins in tibial dyschondroplasia. The current review deeply elaborates on the elevated level of signaling mediators of mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis and the inflammasome. Although investigating these pathways' mechanisms has made significant progress, this review identifies areas where more study is especially required. It might lead to developing innovative therapeutics for tibial dyschondroplasia and other associated bone disorders, e.g., osteoporosis and osteoarthritis, where apoptosis and inflammasome are the significant pathways.
Keywords: apoptosis; chondrocytes; inflammasome; poultry; thiram; tibial dyschondroplasia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chlorogenic acid suppresses mitochondrial apoptotic effectors Bax/Bak to counteract Nod-like receptor pyrin domain 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in thiram exposed chondrocytes.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jan;95:153865. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153865. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 34856474
-
Chlorogenic acid suppresses miR-460a in the regulation of Bcl-2, causing interleukin-1β reduction in thiram exposed chondrocytes via caspase-3/caspase-7 pathway.Phytomedicine. 2022 Sep;104:154296. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154296. Epub 2022 Jul 2. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35809377
-
Cluster of differentiation 147 (CD147) expression is linked with thiram induced chondrocyte's apoptosis via Bcl-2/Bax/Caspase-3 signalling in tibial growth plate under chlorogenic acid repercussion.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021 Apr 15;213:112059. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112059. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021. PMID: 33647747
-
The Molecular Links between Cell Death and Inflammasome.Cells. 2019 Sep 10;8(9):1057. doi: 10.3390/cells8091057. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31509938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homeostatic Regulation of Pro-Angiogenic and Anti-Angiogenic Proteins via Hedgehog, Notch Grid, and Ephrin Signaling in Tibial Dyschondroplasia.Animals (Basel). 2023 Dec 5;13(24):3750. doi: 10.3390/ani13243750. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136788 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms of environmental pollutant-induced cartilage damage: from developmental disorders to osteoarthritis.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Sep;98(9):2763-2796. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03772-9. Epub 2024 May 17. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38758407 Review.
-
Rapid Detection of Malathion, Phoxim and Thiram on Orange Surfaces Using Ag Nanoparticle Modified PDMS as Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Substrate.Foods. 2022 Nov 11;11(22):3597. doi: 10.3390/foods11223597. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36429190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pines M., Reshef R. Sturkie’s Avian Physiology. Elsevier Inc.; New York, NY, USA: 2015. Poultry bone development and bone disorders; pp. 367–377.
-
- Gkiatas I., Lykissas M., Kostas-Agnantis I., Korompilias A., Batistatou A., Beris A. Factors Affecting Bone Growth. Am. J. Orthop. 2015;44:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Huang S.-C., Rehman M.U., Lan Y.-F., Qiu G., Zhang H., Iqbal M.K., Luo H.-q., Mehmood K., Zhang L.-h., Li J.-k. Tibial dyschondroplasia is highly associated with suppression of tibial angiogenesis through regulating the HIF-1α/VEGF/VEGFR signaling pathway in chickens. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:9089. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09664-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

