Expanding the chemical diversity of M13 bacteriophage
- PMID: 36003937
- PMCID: PMC9393631
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.961093
Expanding the chemical diversity of M13 bacteriophage
Abstract
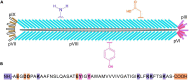
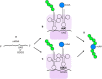
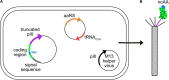
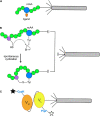
Bacteriophage M13 virions are very stable nanoparticles that can be modified by chemical and genetic methods. The capsid proteins can be functionalized in a variety of chemical reactions without loss of particle integrity. In addition, Genetic Code Expansion (GCE) permits the introduction of non-canonical amino acids (ncAAs) into displayed peptides and proteins. The incorporation of ncAAs into phage libraries has led to the discovery of high-affinity binders with low nanomolar dissociation constant (K D) values that can potentially serve as inhibitors. This article reviews how bioconjugation and the incorporation of ncAAs during translation have expanded the chemistry of peptides and proteins displayed by M13 virions for a variety of purposes.
Keywords: antibody fragments; bioconjugation; combinatorial peptide libraries; cross-linking; cyclization; peptide; phage-display; stop codon suppression.
Copyright © 2022 Allen, Grahn, Kourentzi, Willson, Waldrop, Guo and Kay.
Conflict of interest statement
GA, AG, and BK were employed of a biotech start-up company (Tango Biosciences, Inc.). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Encoding Noncanonical Amino Acids into Phage Displayed Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2676:117-129. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3251-2_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37277628
-
MOrPH-PhD: A Phage Display System for the Functional Selection of Genetically Encoded Macrocyclic Peptides.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2371:261-286. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1689-5_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34596853 Free PMC article.
-
A combinatorial method for constructing libraries of long peptides displayed by filamentous phage.Mol Divers. 1995 Sep;1(1):39-52. doi: 10.1007/BF01715808. Mol Divers. 1995. PMID: 9237193
-
Diversification of Phage-Displayed Peptide Libraries with Noncanonical Amino Acid Mutagenesis and Chemical Modification.Chem Rev. 2024 May 8;124(9):6051-6077. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00004. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 38686960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Biosynthesis of Non-Canonical Amino Acids (ncAAs) and the Methods of ncAAs Incorporation into Proteins.Molecules. 2023 Sep 21;28(18):6745. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186745. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Smartphone-read phage lateral flow assay for point-of-care detection of infection.Analyst. 2023 Feb 13;148(4):839-848. doi: 10.1039/d2an01499h. Analyst. 2023. PMID: 36645184 Free PMC article.
-
Advancement in the development of single chain antibodies using phage display technology.PeerJ. 2024 Apr 10;12:e17143. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17143. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38618563 Free PMC article.
-
Encoding Noncanonical Amino Acids into Phage Displayed Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2676:117-129. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3251-2_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37277628
-
M13 phage: a versatile building block for a highly specific analysis platform.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Jul;415(18):3927-3944. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04606-w. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 36867197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Site-Specific Incorporation of Noncanonical Amino Acids in Synthetic Biology.Chem Rev. 2024 Sep 25;124(18):10577-10617. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00938. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39207844 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

