Characterization of Entry Pathways, Species-Specific Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Residues Determining Entry, and Antibody Neutralization Evasion of Omicron BA.1, BA.1.1, BA.2, and BA.3 Variants
- PMID: 36000843
- PMCID: PMC9472608
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.01140-22
Characterization of Entry Pathways, Species-Specific Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Residues Determining Entry, and Antibody Neutralization Evasion of Omicron BA.1, BA.1.1, BA.2, and BA.3 Variants
Abstract
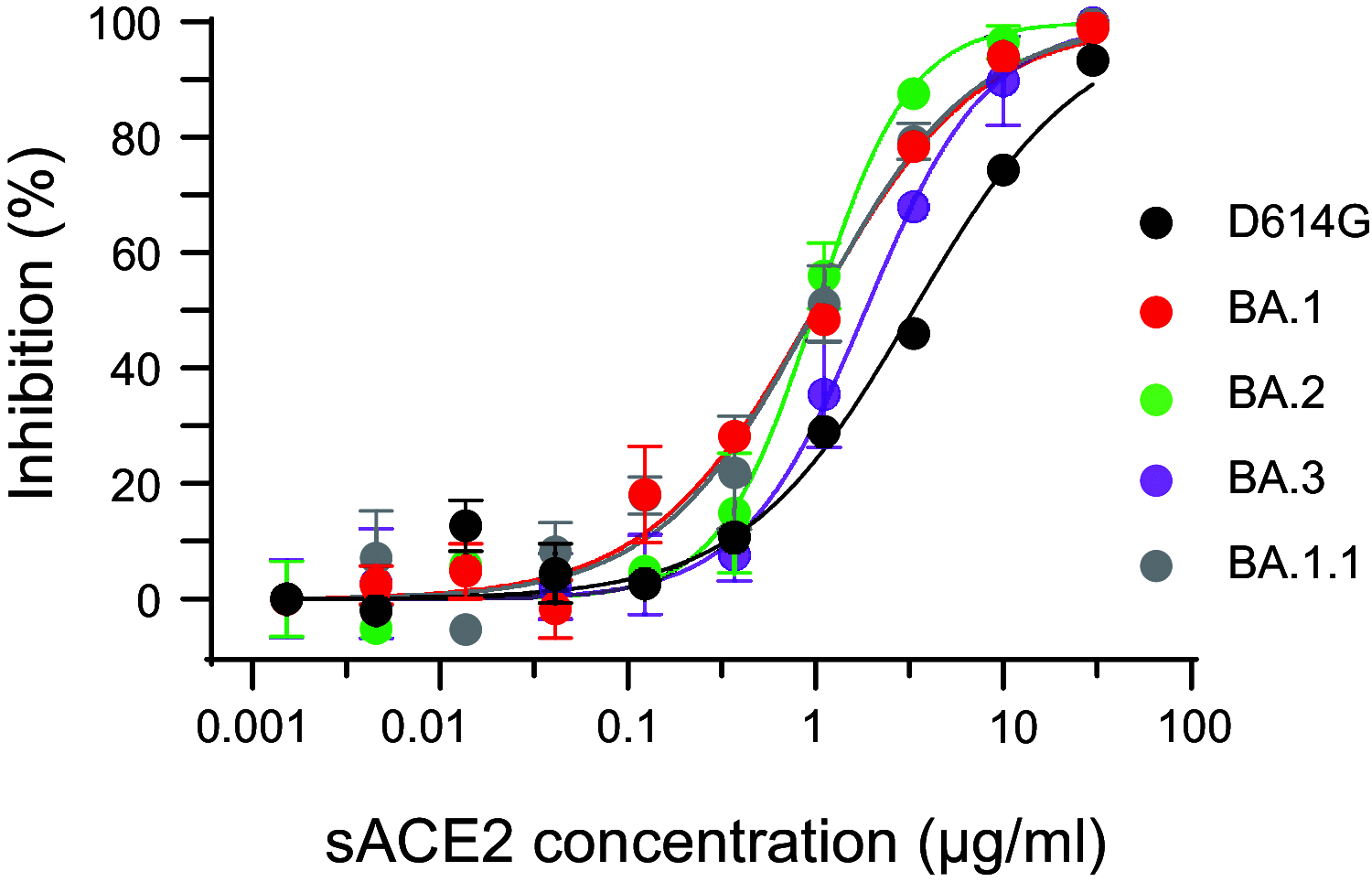
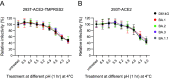
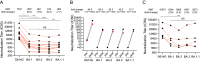
The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants were first detected in November 2021, and several Omicron lineages (BA.1, BA.2, BA.3, BA.4, and BA.5) have since rapidly emerged. Studies characterizing the mechanisms of Omicron variant infection and sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies induced upon vaccination are ongoing by several groups. In the present study, we used pseudoviruses to show that the transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) enhances infection of BA.1, BA.1.1, BA.2, and BA.3 Omicron variants to a lesser extent than ancestral D614G. We further show that Omicron variants have higher sensitivity to inhibition by soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the endosomal inhibitor chloroquine compared to D614G. The Omicron variants also more efficiently used ACE2 receptors from 9 out of 10 animal species tested, and unlike the D614G variant, used mouse ACE2 due to the Q493R and Q498R spike substitutions. Finally, neutralization of the Omicron variants by antibodies induced by three doses of Pfizer/BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine was 7- to 8-fold less potent than the D614G. These results provide insights into the transmissibility and immune evasion capacity of the emerging Omicron variants to curb their ongoing spread. IMPORTANCE The ongoing emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants with an extensive number of spike mutations poses a significant public health and zoonotic concern due to enhanced transmission fitness and escape from neutralizing antibodies. We studied three Omicron lineage variants (BA.1, BA.2, and BA.3) and found that transmembrane serine protease 2 has less influence on Omicron entry into cells than on D614G, and Omicron exhibits greater sensitivity to endosomal entry inhibition compared to D614G. In addition, Omicron displays more efficient usage of diverse animal species ACE2 receptors than D614G. Furthermore, due to Q493R/Q498R substitutions in spike, Omicron, but not D614G, can use the mouse ACE2 receptor. Finally, three doses of Pfizer/BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination elicit high neutralization titers against Omicron variants, although the neutralization titers are still 7- to 8-fold lower those that against D614G. These results may give insights into the transmissibility and immune evasion capacity of the emerging Omicron variants to curb their ongoing spread.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants; animal ACE2 receptors; breakthrough infections; neutralization resistance; transmembrane serine protease 2; vaccine booster; virus entry pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.5: Evolving tropism and evasion of potent humoral responses and resistance to clinical immunotherapeutics relative to viral variants of concern.EBioMedicine. 2022 Oct;84:104270. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104270. Epub 2022 Sep 18. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 36130476 Free PMC article.
-
AlphaFold2 Modeling and Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Conformational Ensembles for the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Omicron JN.1, KP.2 and KP.3 Variants: Mutational Profiling of Binding Energetics Reveals Epistatic Drivers of the ACE2 Affinity and Escape Hotspots of Antibody Resistance.Viruses. 2024 Sep 13;16(9):1458. doi: 10.3390/v16091458. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339934 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Spike Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern on Human or Animal ACE2-Mediated Virus Entry and Neutralization.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0178921. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01789-21. Epub 2022 May 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35638818 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain and their delicate balance between ACE2 affinity and antibody evasion.Protein Cell. 2024 May 28;15(6):403-418. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwae007. Protein Cell. 2024. PMID: 38442025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Entry Related Viral and Host Genetic Variations: Implications on COVID-19 Severity, Immune Escape, and Infectivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 17;22(6):3060. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063060. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence among Canadian Blood Donors: The Advance of Omicron.Viruses. 2022 Oct 25;14(11):2336. doi: 10.3390/v14112336. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36366432 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of mutations defining SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.2.12.1 and BA.4/5 on Spike function and neutralization.iScience. 2023 Oct 27;26(11):108299. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108299. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38026181 Free PMC article.
-
The SARS-CoV-2 Spike is a virulence determinant and plays a major role on the attenuated phenotype of Omicron virus in a feline model of infection.J Virol. 2024 Mar 19;98(3):e0190223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01902-23. Epub 2024 Feb 29. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38421180 Free PMC article.
-
Smoke and Spike: Benzo[a]pyrene Enhances SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Boosting NR4A2-Induced ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Expression.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Sep;10(26):e2300834. doi: 10.1002/advs.202300834. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37428471 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation and Degeneration of SARS-CoV-2 Despite Adaptive Evolution.Cureus. 2023 Jan 3;15(1):e33316. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33316. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36741655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lusvarghi S, Pollett SD, Neerukonda SN, Wang W, Wang R, Vassell R, Epsi NJ, Fries AC, Agan BK, Lindholm DA, Colombo CJ, Mody R, Ewers EC, Lalani T, Ganesan A, Goguet E, Hollis-Perry M, Coggins SAA, Simons MP, Katzelnick LC, Wang G, Tribble DR, Bentley L, Eakin AE, Broder CC, Erlandson KJ, Laing ED, Burgess TH, Mitre E, Weiss CD. 2022. SARS-CoV-2 BA.1 variant is neutralized by vaccine booster-elicited serum but evades most convalescent serum and therapeutic antibodies. Sci Transl Med 14:eabn8543. 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn8543. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cele S, Jackson L, Khoury DS, Khan K, Moyo-Gwete T, Tegally H, San JE, Cromer D, Scheepers C, Amoako DG, Karim F, Bernstein M, Lustig G, Archary D, Smith M, Ganga Y, Jule Z, Reedoy K, Hwa S-H, Giandhari J, Blackburn JM, Gosnell BI, Abdool Karim SS, Hanekom W, Davies M-A, Hsiao M, Martin D, Mlisana K, Wibmer CK, Williamson C, York D, Harrichandparsad R, Herbst K, Jeena P, Khoza T, Kløverpris H, Leslie A, Madansein R, Magula N, Manickchund N, Marakalala M, Mazibuko M, Moshabela M, Mthabela N, Naidoo K, Ndhlovu Z, Ndung’u T, Ngcobo N, Nyamande K, Patel V, COMMIT-KZN Team , et al. 2022. Omicron extensively but incompletely escapes Pfizer BNT162b2 neutralization. Nature 602:654–656. 10.1038/s41586-021-04387-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cameroni E, Bowen JE, Rosen LE, Saliba C, Zepeda SK, Culap K, Pinto D, VanBlargan LA, De Marco A, di Iulio J, Zatta F, Kaiser H, Noack J, Farhat N, Czudnochowski N, Havenar-Daughton C, Sprouse KR, Dillen JR, Powell AE, Chen A, Maher C, Yin L, Sun D, Soriaga L, Bassi J, Silacci-Fregni C, Gustafsson C, Franko NM, Logue J, Iqbal NT, Mazzitelli I, Geffner J, Grifantini R, Chu H, Gori A, Riva A, Giannini O, Ceschi A, Ferrari P, Cippà PE, Franzetti-Pellanda A, Garzoni C, Halfmann PJ, Kawaoka Y, Hebner C, Purcell LA, Piccoli L, Pizzuto MS, Walls AC, Diamond MS, et al. 2022. Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift. Nature 602:664–670. 10.1038/s41586-021-04386-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

