ACE2 and TMPRSS2 SNPs as Determinants of Susceptibility to, and Severity of, a COVID-19 Infection
- PMID: 35996506
- PMCID: PMC8915702
- DOI: 10.3389/bjbs.2021.10238
ACE2 and TMPRSS2 SNPs as Determinants of Susceptibility to, and Severity of, a COVID-19 Infection
Abstract
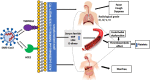
Background: Genetic risk factors may be related to the infectivity and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and host transmembrane serine protease (TMPRSS2) have key role in viral cell entrance and priming. Methods: This case-control study on 147 healthy controls and 299 COVID-19 patients identified potential determinants and risk factors, including gene polymorphism involved in the severity (mild, moderate, severe) of COVID-19 disease defined by CORAD radiological criteria. Results: The ACE2 s2285666 and TMPRSS2 rs12329760 SNPs were significantly linked with COVID-19 disease severity, as were certain co-morbidities (hypertension, heart disease) and laboratory parameters. Both SNPs were amongst the highest predictors of disease severity: TMPRSS2 rs12329760 CT + TT [odds ratio (95% CI) 17.6 (5.1-61.10), ACE2 rs2285666 CT + TT 9.9 (3.2-30.9), both p < 0.001]. There was an increase in the expression of genotype frequencies of ACE2 rs2285666 and TMPRSS2 rs1232976 (TT), (CT + TT), and (T) allele in severe COVID-19 group compared to control and mild groups. Disease severity was also linked to elevated CRP, ferritin and D-dimer, and lower lymphocytes and platelet count (all p < 0.001). Conclusion: ACE2 rs2285666 and TMPRSS2 rs12329760 SNPs, in addition to lymphocyte count, CRP, D-dimers, ferritin, and hypertension, are predictors of COVID-19 disease severity.
Keywords: ACE2 gene; TMPRSS2 gene; cytokine storm; determinants of COVID-19 disease; genetic susceptibility of COVID-19; thromboembolic complications.
Copyright © 2022 Abdelsattar, Kasemy, Ewida, Abo-Elsoud, Zytoon, Abdelaal, Abdelgawad, Khalil and Kamel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic association of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms with COVID-19 severity; a single centre study from Egypt.Virol J. 2024 Jan 23;21(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02298-x. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38263160 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms on COVID-19 outcome and disease severity in adult patients: A prospective cohort study in a tertiary hospital, Indonesia.Narra J. 2024 Aug;4(2):e919. doi: 10.52225/narra.v4i2.919. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Narra J. 2024. PMID: 39280326 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphisms of ACE1, ACE2, and TMPRSS2 associated with COVID-19 severity: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Rev Med Virol. 2022 Jul;32(4):e2323. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2323. Epub 2022 Jan 8. Rev Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34997794 Review.
-
Genetic Association between ACE2 (rs2285666 and rs2074192) and TMPRSS2 (rs12329760 and rs2070788) Polymorphisms with Post-COVID Symptoms in Previously Hospitalized COVID-19 Survivors.Genes (Basel). 2022 Oct 24;13(11):1935. doi: 10.3390/genes13111935. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360172 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphisms of ACE1, ACE2, IFTM3, TMPRSS2 and TNFα genes associated with susceptibility and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Nov;23(7):3251-3264. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01038-9. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37055652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relevance of HLA-DP/DQ and INF-λ4 Polymorphisms to COVID-19 Outcomes.Br J Biomed Sci. 2023 Jan 20;80:11044. doi: 10.3389/bjbs.2023.11044. eCollection 2023. Br J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 36743382 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms within the SARS-CoV-2 Human Receptor Genes Associate with Variable Disease Outcomes across Ethnicities.Genes (Basel). 2023 Sep 14;14(9):1798. doi: 10.3390/genes14091798. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761938 Free PMC article.
-
Association of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 genes variants with disease severity and most important biomarkers in COVID-19 patients in Bosnia and Herzegovina.Croat Med J. 2024 Jun 13;65(3):220-231. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2024.65.220. Croat Med J. 2024. PMID: 38868968 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Candidate Biomarkers.Eurasian J Med. 2022 Dec;54(Suppl1):16-22. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2022.22305. Eurasian J Med. 2022. PMID: 36655440 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic association of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphisms with COVID-19 severity; a single centre study from Egypt.Virol J. 2024 Jan 23;21(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02298-x. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38263160 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous