Analysis and Prediction of the Survival Trends of Patients with Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Model-Based Period Analysis, 2001-2015
- PMID: 35981235
- PMCID: PMC9393668
- DOI: 10.1177/10732748221121226
Analysis and Prediction of the Survival Trends of Patients with Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Model-Based Period Analysis, 2001-2015
Abstract
Background: Clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors worldwide whose poor prognosis results in a serious disease burden on patients. The changing trend of the long-term relative survival rates (RSRs) of patients with ccRCC was analyzed in this study to evaluate their treatment results over a 15-year period.
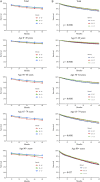
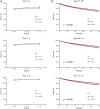
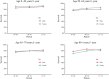
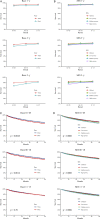
Methods: This study is a retrospective study, which assessed and predicted the 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates of patients with ccRCC during 2001-2005, 2006-2010, 2011-2015, and 2016-2020 using data extracted from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. Period analysis was used in this study to analyze the data from the SEER database and to assess survival differences according to age, sex, race, and socioeconomic status (SES) during the 15-year study period by comparing Kaplan-Meier curves.
Results: During 2001-2015, the 5-year RSR of patients with ccRCC increased from 78.4% to 83.0%, and the generalized linear model predicted that the 5-year RSR increased to 85.7% during 2016-2020. The RSR of patients with ccRCC differed significantly with SES, race, sex, and age. Compared with male patients, the survival advantage of female patients decreased as their age increased. The RSR of all patients with ccRCC was also lower in patients with a lower SES and of black race.
Conclusion: This study found an improvement in the RSR of patients with ccRCC during 2001-2020. Understanding the change trend of the survival rate of patients with ccRCC is helpful to improve the design of clinical trials. It also provides basic data and a scientific basis for evaluating the harm of ccRCC on the health of affected patients and the effect of cancer prevention, and developing cancer prevention plans.
Keywords: clear cell renal cell carcinoma; period analysis; relative survival rate; sex; socioeconomic status; surveillance, epidemiology, and end results.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does chromophobe renal cell carcinoma have better survival than clear cell renal cell carcinoma? A clinical-based cohort study and meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Feb;48(2):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s11255-015-1161-3. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26589610 Review.
-
53 years old is a reasonable cut-off value to define young and old patients in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a study based on TCGA and SEER database.BMC Cancer. 2021 May 29;21(1):638. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08376-5. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34051738 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation and Prediction Analysis of 3- and 5-Year Relative Survival Rates of Patients with Cervical Cancer: A Model-Based Period Analysis.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241232324. doi: 10.1177/10732748241232324. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 38408865 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive subgroup analyses of survival outcomes between clear cell renal cell adenocarcinoma and papillary renal cell adenocarcinoma.Cancer Med. 2020 Dec;9(24):9409-9418. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3563. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 33141518 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Comparing the Effectiveness and Adverse Effects of Different Systemic Treatments for Non-clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2017 Mar;71(3):426-436. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.11.020. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27939075 Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

