Stem cell membrane-camouflaged targeted delivery system in tumor
- PMID: 35967738
- PMCID: PMC9364095
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100377
Stem cell membrane-camouflaged targeted delivery system in tumor
Abstract
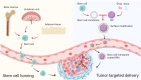
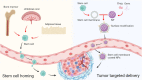
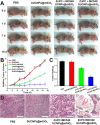
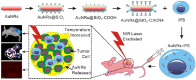
Cell membrane-coated nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted growing attention in the field of targeted delivery strategies, which successfully combine the advantages and properties of both cell membranes and synthetic NPs. Stem cell-based delivery systems have the innate targeting capability to tumor tissues, but inappropriate stem cells might promote tumor growth after being injected into the body. Accordingly, it is urgent to explore novel drug delivery systems that might combine the advantages of stem cells and eliminate the possible risks. This review aimed to investigate the stem cell membrane-camouflaged targeted delivery system in tumors. We discussed the underlying mechanisms of stem cell homing to target tumors. Then, the common membrane modification methods well as preparation methods of stem cell membrane coated NPs were concluded. NPs coating the stem cell membranes could obtain the tumor targeting ability, enhanced biocompatibility, and effective drug loading. Furthermore, we investigated the potential clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells membrane-camouflaged targeted delivery systems for anti-tumor therapies, such as chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy, magnetic hyperthermia therapy and imaging, CRISPR-Cas9 gene therapy, and synergistic therapy. Taken together, stem cell membrane-coated NPs hold the tremendous prospect for biomedical applications in tumor therapy.
Keywords: Membrane coated nanoparticles; Stem cell; Stem cell homing; Tumor targeting therapy.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stem cell membrane, stem cell-derived exosomes and hybrid stem cell camouflaged nanoparticles: A promising biomimetic nanoplatforms for cancer theranostics.J Control Release. 2022 Aug;348:706-722. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.026. Epub 2022 Jun 22. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35732250 Review.
-
Macrophage membrane-camouflaged biomimetic nanovesicles for targeted treatment of arthritis.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Mar;95:102241. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102241. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38387516 Review.
-
Polydopamine Nanoparticles Camouflaged by Stem Cell Membranes for Synergistic Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Malignant Bone Tumors.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Dec 14;15:10183-10197. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S282931. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33363374 Free PMC article.
-
Biomembrane camouflaged nanoparticles: A paradigm shifts in targeted drug delivery system.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024 Jun;238:113893. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2024.113893. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024. PMID: 38631282 Review.
-
Current progress of mesenchymal stem cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles for targeted therapy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 May;161:114451. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114451. Epub 2023 Mar 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36870279 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomimetic Nano-Drug Delivery System: An Emerging Platform for Promoting Tumor Treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jan 18;19:571-608. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S442877. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38260239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of advanced biomaterials in photothermal therapy for malignant bone tumors.Biomater Res. 2023 Nov 15;27(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s40824-023-00453-z. Biomater Res. 2023. PMID: 37968707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell membrane-coated nanoconstructs: why have they not yet found a home in clinical practice?Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024 Jul 14;19(17):1507-1510. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2369495. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38953891 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Homologous cell membrane-based hydrogel creates spatiotemporal niches to improve outcomes of dysregulated chronic wound healing.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Sep 14;28:101243. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101243. eCollection 2024 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39315394 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-nanocarrier drug delivery system: a promising strategy for cancer therapy.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Mar;14(3):581-596. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01429-1. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 37721694 Review.
References
-
- Thanuja M.Y., Anupama C., Ranganath S.H. Bioengineered cellular and cell membrane-derived vehicles for actively targeted drug delivery: so near and yet so far. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018;132:57–80. - PubMed
-
- Wu H.H., Zhou Y., Tabata Y., Gao J.Q. Mesenchymal stem cell-based drug delivery strategy: from cells to biomimetic. J. Contr. Release. 2019;294:102–113. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K., Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

