Androgen receptor signaling and spatial chromatin organization in castration-resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 35966880
- PMCID: PMC9372301
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.924087
Androgen receptor signaling and spatial chromatin organization in castration-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
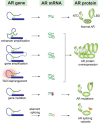
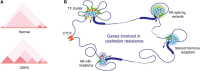
Prostate cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer death and affects millions of men in the world. The American Cancer Society estimated about 34,500 deaths from prostate cancer in the United States in year 2022. The Androgen receptor (AR) signaling is a major pathway that sustains local and metastatic prostate tumor growth. Androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT) is the standard of care for metastatic prostate cancer patient and can suppress the tumor growth for a median of 2-3 years. Unfortunately, the malignancy inevitably progresses to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) which is more aggressive and no longer responsive to ADT. Surprisingly, for most of the CPRC patients, cancer growth still depends on androgen receptor signaling. Accumulating evidence suggests that CRPC cells have rewired their transcriptional program to retain AR signaling in the absence of androgens. Besides AR, other transcription factors also contribute to the resistance mechanism through multiple pathways including enhancing AR signaling pathway and activating other complementary signaling pathways for the favor of AR downstream genes expression. More recent studies have shown the role of transcription factors in reconfiguring chromatin 3D structure and regulating topologically associating domains (TADs). Pioneer factors, transcription factors and coactivators form liquid-liquid phase separation compartment that can modulate transcriptional events along with configuring TADs. The role of AR and other transcription factors on chromatin structure change and formation of condensate compartment in prostate cancer cells has only been recently investigated and appreciated. This review intends to provide an overview of transcription factors that contribute to AR signaling through activation of gene expression, governing 3D chromatin structure and establishing phase to phase separation. A more detailed understanding of the spatial role of transcription factors in CRPC might provide novel therapeutic targets for the treatment of CRPC.
Keywords: TAD; androgen; castration resistant; phase separation; prostate cancer; steroid hormone receptor.
Copyright © 2022 Zhou and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Androgen receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Dec;140(3):223-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23859952 Review.
-
Androgen receptor-dependent and -independent mechanisms driving prostate cancer progression: Opportunities for therapeutic targeting from multiple angles.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3724-3745. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12554. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27741508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between orphan nuclear receptors and androgen receptor-dependent or-independent growth signalings in prostate cancer.Mol Aspects Med. 2021 Apr;78:100921. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2020.100921. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Mol Aspects Med. 2021. PMID: 33121737 Review.
-
Targeting the androgen receptor signaling pathway in advanced prostate cancer.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2022 Jul 22;79(15):1224-1235. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxac105. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35390118 Review.
-
MicroRNA Regulation of Androgen Receptor in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Premises, Promises, and Potentials.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 25;14(4):559-569. doi: 10.2174/1874467213666201223121850. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33357209 Review.
Cited by
-
The cancer testis antigen TDRD1 regulates prostate cancer proliferation by associating with snRNP biogenesis machinery.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 22:rs.3.rs-2035901. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2035901/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Oncogene. 2023 Jun;42(22):1821-1831. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02690-x PMID: 36865141 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Comparative analysis of novel hormonal agents in non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A Taiwanese perspective.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 7;19(8):e0306900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306900. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39110673 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing the Reciprocal Crosstalk between the AR and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways for Prostate Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 24;24(3):2289. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032289. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factor condensates and signaling driven transcription.Nucleus. 2023 Dec;14(1):2205758. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2023.2205758. Nucleus. 2023. PMID: 37129580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

