The role of blood CXCL12 level in prognosis of coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 35966557
- PMCID: PMC9363627
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.938540
The role of blood CXCL12 level in prognosis of coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: The role of C-X-C motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12) in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases (ASCVDs) has emerged as one of the research hotspots in recent years. Studies reported that the higher blood CXCL12 level was associated with increased major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), but the results were inconsistent. The objective of this study was to clarify the prognostic value of the blood CXCL12 level in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) through meta-analysis.
Methods: All related studies about the association between the blood CXCL12 level and the prognosis of CAD were comprehensively searched and screened according to inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria. The quality of the included literature was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS). The heterogeneity test was conducted, and the pooled hazard risk (HR) or the odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated using the fixed-effect or random-effects model accordingly. Publication bias was evaluated using Begg's funnel plot and Egger's test. Sensitivity analysis and subgroup analysis were also conducted.
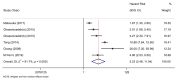
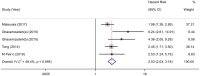
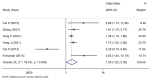
Results: A total of 12 original studies with 2,959 CAD subjects were included in the final data combination. The pooled data indicated a significant association between higher CXCL12 levels and MACEs both in univariate analysis (HR 5.23, 95% CI 2.48-11.04) and multivariate analysis (HR 2.53, 95% CI 2.03-3.16) in the CXCL12 level as the category variable group. In the CXCL12 level as the continuous variable group, the result also indicated that the higher CXCL12 level significantly predicted future MACEs (multivariate OR 1.55, 95% CI 1.02-2.35). Subgroup analysis of the CXCL12 level as the category variable group found significant associations in all acute coronary syndrome (ACS) (univariate HR 9.72, 95% CI 4.69-20.15; multivariate HR 2.47, 95% CI 1.79-3.40), non-ACS (univariate HR 2.73, 95% CI 1.65-4.54; multivariate HR 3.49, 95% CI 1.66-7.33), Asian (univariate HR 7.43, 95% CI 1.70-32.49; multivariate HR 2.21, 95% CI 1.71-2.85), Caucasian (univariate HR 3.90, 95% CI 2.73-5.57; multivariate HR 3.87, 95% CI 2.48-6.04), short-term (univariate HR 9.36, 95% CI 4.10-21.37; multivariate HR 2.72, 95% CI 1.97-3.76), and long-term (univariate HR 2.86, 95% CI 1.62-5.04; multivariate HR 2.38, 95% CI 1.76-3.22) subgroups. Subgroup analysis of the CXCL12 level as the continuous variable group found significant associations in non-ACS (multivariate OR 1.53, 95% CI 1.23-1.92), Caucasian (multivariate OR 3.83, 95% CI 1.44-10.19), and long-term (multivariate OR 1.62, 95% CI 1.37-1.93) subgroups, but not in ACS (multivariate OR 1.36, 95% CI 0.67-2.75), Asian (multivariate OR 1.40, 95% CI 0.91-2.14), and short-term (multivariate OR 1.16, 95% CI 0.28-4.76) subgroups. No significant publication bias was found in this meta-analysis.
Conclusion: The higher blood CXCL12 level is associated with increased MACEs in patients with CAD, and the blood CXCL12 level may serve as an important prognostic index for CAD. Integrating the blood CXCL12 level into CAD risk assessment tools may provide more comprehensive messages for evaluating and managing patients with CAD.
Keywords: CXCL12; MACEs; acute coronary syndrome; coronary artery disease; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Ding, Feng and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Meta analysis of whether cytoreductive surgery combined with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy can improve survival in patients with colorectal cancer peritoneal metastasis].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Mar 25;24(3):256-263. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20201111-00604. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34645170 Chinese.
-
The association between soluble suppression of tumorigenicity-2 and long-term prognosis in patients with coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 4;15(9):e0238775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238775. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32886697 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of malnutrition in patients with coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Nutr Rev. 2024 Aug 1;82(8):1013-1027. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad108. Nutr Rev. 2024. PMID: 37665731
-
Remnant-Like Particle Cholesterol and the Risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Dec 11;9(12):452. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9120452. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022. PMID: 36547449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index and the incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis of cohort studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Apr 3;20(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01268-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33812373 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting immune cell recruitment in atherosclerosis.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024 Nov;21(11):824-840. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01023-z. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38664575 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

