Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate depletion by statins compromises skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity
- PMID: 35961942
- PMCID: PMC9745480
- DOI: 10.1002/jcsm.13061
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate depletion by statins compromises skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity
Abstract
Background: Statins are widely prescribed cholesterol-lowering drugs but have been shown to increase the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the diabetogenic effect of statins are still not fully understood.
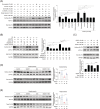
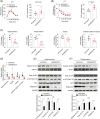
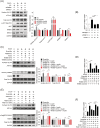
Methods: The effects of geranylgeranyl transferase I and II (GGTase I and II) inhibition on insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and GLUT4 translocation, and the dependence of these effects on insulin signalling were investigated in skeletal muscle cells. The protective effects of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) and its precursor geranylgeraniol (GGOH) on simvastatin-induced insulin resistance were evaluated in vitro and in vivo. The effect of GGTase II inhibition in skeletal muscle on insulin sensitivity in vivo was confirmed by adeno-associated virus serotype 9 (AAV9)-mediated knockdown of the specific subunit of GGTase II, RABGGTA. The regulatory mechanisms of GGTase I on insulin signalling and GGTase II on insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation were investigated by knockdown of RhoA, TAZ, IRS1, geranylgeranylation site mutation of RhoA, RAB8A, and RAB13.
Results: Both inhibition of GGTase I and II mimicked simvastatin-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells. GGPP and GGOH were able to prevent simvastatin-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance in vitro and in vivo. GGTase I inhibition suppressed the phosphorylation of AKT (Ser473) (-51.3%, P < 0.01), while GGTase II inhibition had no effect on it. AAV9-mediated knockdown of RABGGTA in skeletal muscle impaired glucose disposal without disrupting insulin signalling in vivo (-46.2% for gastrocnemius glucose uptake, P < 0.001; -52.5% for tibialis anterior glucose uptake, P < 0.001; -17.8% for soleus glucose uptake, P < 0.05; -31.4% for extensor digitorum longus glucose uptake, P < 0.01). Inhibition of RhoA, TAZ, IRS1, or geranylgeranylation deficiency of RhoA attenuated the beneficial effect of GGPP on insulin signalling in skeletal muscle cells. Geranylgeranylation deficiency of RAB8A inhibited insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation and concomitant glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cells (-42.8% for GLUT4 translocation, P < 0.01; -50.6% for glucose uptake, P < 0.001).
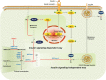
Conclusions: Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate regulates glucose uptake via GGTase I-mediated insulin signalling-dependent way and GGTase II-mediated insulin signalling-independent way in skeletal muscle. Supplementation of GGPP/GGOH could be a potential therapeutic strategy for statin-induced insulin resistance.
Keywords: GGPP; Insulin resistance; RAB8A; RhoA; Skeletal muscle; Statin.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society on Sarcopenia, Cachexia and Wasting Disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Lai Wang, Zuguo Zheng, Lijun Zhu, Lingchang Meng, Hanling Liu, Keke Wang, Jun Chen, Ping Li, and Hua Yang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mevalonate pathway orchestrates insulin signaling via RAB14 geranylgeranylation-mediated phosphorylation of AKT to regulate hepatic glucose metabolism.Metabolism. 2022 Mar;128:155120. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.155120. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Metabolism. 2022. PMID: 34995578
-
Mechanisms of insulin resistance by simvastatin in C2C12 myotubes and in mouse skeletal muscle.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;164:23-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.02.025. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30796916
-
Simvastatin induces insulin resistance in L6 skeletal muscle myotubes by suppressing insulin signaling, GLUT4 expression and GSK-3β phosphorylation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Nov 11;480(2):194-200. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.026. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27743890
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human dermal microvascular endothelial cells offer new insights into the relationship between lipid metabolism and angiogenesis.Stem Cell Rev. 2006;2(2):93-102. doi: 10.1007/s12015-006-0015-x. Stem Cell Rev. 2006. PMID: 17237547 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential role of geranylgeraniol in managing statin-associated muscle symptoms: a COVID-19 related perspective.Front Physiol. 2023 Nov 17;14:1246589. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1246589. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38046949 Free PMC article.
-
The Biomedical Importance of the Missing Pathway for Farnesol and Geranylgeraniol Salvage.Molecules. 2022 Dec 8;27(24):8691. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248691. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36557825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rationally designed CD19 monoclonal antibody-triptolide conjugate for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Oct;14(10):4560-4576. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.06.024. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39525579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cederberg H, Stančáková A, Yaluri N, Modi S, Kuusisto J, Laakso M. Increased risk of diabetes with statin treatment is associated with impaired insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion: a 6 year follow‐up study of the METSIM cohort. Diabetologia 2015;58:1109–1117. - PubMed
-
- Henriksbo BD, Lau TC, Cavallari JF, Denou E, Chi W, Lally JS, et al. Fluvastatin causes NLRP3 inflammasome‐mediated adipose insulin resistance. Diabetes 2014;63:3742–3747. - PubMed
-
- Shen L, Gu Y. Atorvastatin targets the islet mevalonate pathway to dysregulate mTOR signaling and reduce β‐cell functional mass. Diabetes 2020;69:48–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

