Thiocoumarins: From the Synthesis to the Biological Applications
- PMID: 35956851
- PMCID: PMC9369797
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154901
Thiocoumarins: From the Synthesis to the Biological Applications
Abstract
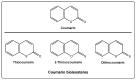
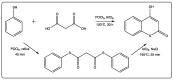
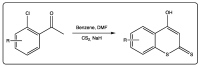
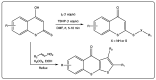
Coumarin is a privilege scaffold in medicinal chemistry. Coumarin derivatives are still an emerging class of highly potent pharmaceutical drugs, best known in the field of antimicrobials and anticoagulants. Thiocoumarins are a particular class of coumarins in which one or two of the oxygen atoms are replaced by a sulfur. They are chemically subdivided in three groups: Thiocoumarins, 2-thioxocoumarins, and dithiocoumarins. This review emphasizes the rationale behind the synthesis and biological applications of the most relevant publications related to this family of compounds. Particular attention has been given to their potential as drug candidates, with particular emphasis in the last 5 years. This article is based on the most relevant information collected from multiple electronic databases, including SciFinder, Pubmed, Espacenet, and Mendeley.
Keywords: 2-thioxocoumarins; biological applications; dithiocoumarins; synthesis; thiocoumarins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3-Phenylcoumarins as a Privileged Scaffold in Medicinal Chemistry: The Landmarks of the Past Decade.Molecules. 2021 Nov 8;26(21):6755. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216755. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34771164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trending Topics on Coumarin and Its Derivatives in 2020.Molecules. 2021 Jan 19;26(2):501. doi: 10.3390/molecules26020501. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33477785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Biologically Active Coumarins from Marine Sources: Synthesis and Evaluation.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 31;21(1):37. doi: 10.3390/md21010037. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36662210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computer-aided Design of Coumarins for Neurodegenerative Diseases: Trends of the Last Decade.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(25):2245-2257. doi: 10.2174/1568026621666211011101429. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34635041 Review.
-
Synthetic and natural coumarins as potent anticonvulsant agents: A review with structure-activity relationship.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Jul;47(7):915-931. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13644. Epub 2022 Mar 15. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 35288962 Review.
Cited by
-
Tuning singlet oxygen generation with caged organic photosensitizers.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 3;15(1):7689. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51872-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39227575 Free PMC article.
-
Blue and Green Light Responsive Caged Glutamate.J Photochem Photobiol A Chem. 2024 Jan 15;447:115183. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2023.115183. Epub 2023 Sep 18. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem. 2024. PMID: 37928883
-
Design, Synthesis and Fungicidal Activity of Ester Derivatives of 4-(3,4-Dichloroisothiazole) 7-Hydroxy Coumarin.Molecules. 2023 Jul 4;28(13):5205. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135205. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nagy P.I. Replacement of oxygen by sulfur in small organic molecules. 3. Theoretical studies on the tautomeric equilibria of the 2OH and 4OH-substituted oxazole and thiazole and the 3OH and 4OH-substituted isoxazole and isothiazole in the isolated state and in solution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016;17:1094. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary D., Pramanik T., Santra S. Thiocoumarins and dithiocoumarins: Advances in Synthesis and Pharmacological Activity. Curr. Org. Chem. 2020;24:1793–1814. doi: 10.2174/1385272824999200812132707. - DOI
-
- Meth-Cohn O., Tarnowski B. Thiocoumarins. In: Katritzky A.R., Boulton A.J., editors. Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 1980. pp. 115–133.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

