Emodin Sensitizes Cervical Cancer Cells to Vinblastine by Inducing Apoptosis and Mitotic Death
- PMID: 35955645
- PMCID: PMC9369386
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158510
Emodin Sensitizes Cervical Cancer Cells to Vinblastine by Inducing Apoptosis and Mitotic Death
Abstract
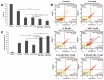
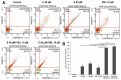
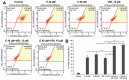
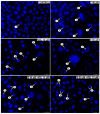
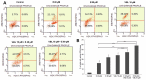
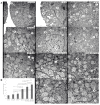
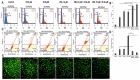
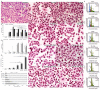
In recent years, studies on the effects of combining novel plant compounds with cytostatics used in cancer therapy have received considerable attention. Since emodin sensitizes tumor cells to chemotherapeutics, we evaluated changes in cervical cancer cells after its combination with the antimitotic drug vinblastine. Cellular changes were demonstrated using optical, fluorescence, confocal and electron microscopy. Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay. The level of apoptosis, caspase 3/7, Bcl-2 protein, ROS, mitochondrial membrane depolarization, cell cycle and degree of DNA damage were analyzed by flow cytometry. The microscopic image showed indicators characteristic for emodin- and vinblastine-induced mitotic catastrophe, i.e., multinucleated cells, giant cells, cells with micronuclei, and abnormal mitotic figures. These compounds also increased blocking of cells in the G2/M phase, and the generated ROS induced swelling and mitochondrial damage. This translated into the growth of apoptotic cells with active caspase 3/7 and inactivation of Bcl-2 protein and active ATM kinase. Emodin potentiated the cytotoxic effect of vinblastine, increasing oxidative stress, mitotic catastrophe and apoptosis. Preliminary studies show that the combined action of both compounds, may constitute an interesting form of anticancer therapy.
Keywords: apoptosis; emodin; mitotic death; oxidative stress; vinblastine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emodin Induces Death in Human Cervical Cancer Cells Through Mitotic Catastrophe.Anticancer Res. 2019 Feb;39(2):679-686. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13163. Anticancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30711945
-
The Multidirectional Effect of Azelastine Hydrochloride on Cervical Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 24;23(11):5890. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115890. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682572 Free PMC article.
-
Physcion Induces Potential Anticancer Effects in Cervical Cancer Cells.Cells. 2021 Aug 8;10(8):2029. doi: 10.3390/cells10082029. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440797 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Mitotic Catastrophe in Human Cervical Cancer Cells After Administration of Aloe-emodin.Anticancer Res. 2018 Apr;38(4):2037-2044. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12443. Anticancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29599321
-
Emodin induces apoptosis of human tongue squamous cancer SCC-4 cells through reactive oxygen species and mitochondria-dependent pathways.Anticancer Res. 2009 Jan;29(1):327-35. Anticancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19331169
Cited by
-
Insight into the Biological Roles and Mechanisms of Phytochemicals in Different Types of Cancer: Targeting Cancer Therapeutics.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 31;15(7):1704. doi: 10.3390/nu15071704. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the mechanism of emodin-induced hepatotoxicity.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 25;10(13):e33631. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33631. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39027614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparative analysis of phyto-components on EGFR binding, viability, and migration in HPV positive ME180 and HPV negative C33A cervical cancer cells.Med Oncol. 2023 Nov 14;40(12):357. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02223-2. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37964051
-
Vinblastine Resistance Is Associated with Nephronophthisis 3-Mediated Primary Cilia via Intraflagellar Transport Protein 88 and Apoptosis-Antagonizing Transcription Factor.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 26;25(19):10369. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910369. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408701 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

