Cardiotoxicity of Zebrafish Induced by 6-Benzylaminopurine Exposure and Its Mechanism
- PMID: 35955574
- PMCID: PMC9369308
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23158438
Cardiotoxicity of Zebrafish Induced by 6-Benzylaminopurine Exposure and Its Mechanism
Abstract
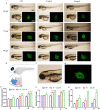
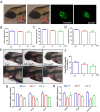
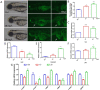
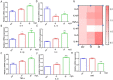
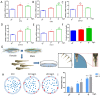
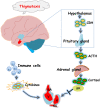
6-BA is a common plant growth regulator, but its safety has not been conclusive. The heart is one of the most important organs of living organisms, and the cardiogenesis process of zebrafish is similar to that of humans. Therefore, based on wild-type and transgenic zebrafish, we explored the development of zebrafish heart under 6-BA exposure and its mechanism. We found that 6-BA affected larval cardiogenesis, inducing defective expression of key genes for cardiac development (myl7, vmhc, and myh6) and AVC differentiation (bmp4, tbx2b, and notch1b), ultimately leading to weakened cardiac function (heart rate, diastolic speed, systolic speed). Acridine orange staining showed that the degree of apoptosis in zebrafish hearts was significantly increased under 6-BA, and the expression of cell-cycle-related genes was also changed. In addition, HPA axis assays revealed abnormally expressed mRNA levels of genes and significantly increased cortisol contents, which was also consistent with the observed anxiety behavior in zebrafish at 3 dpf. Transcriptional abnormalities of pro- and anti-inflammatory factors in immune signaling pathways were also detected in qPCR experiments. Collectively, we found that 6-BA induced cardiotoxicity in zebrafish, which may be related to altered HPA axis activity and the onset of inflammatory responses under 6-BA treatment.
Keywords: 6-benzylaminopurine; HPA axis activity; cardiotoxicity; inflammation; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exposure to acrylamide induces cardiac developmental toxicity in zebrafish during cardiogenesis.Environ Pollut. 2018 Mar;234:656-666. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.095. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Environ Pollut. 2018. PMID: 29223822
-
Developmental toxicity and alteration of gene expression in zebrafish embryo exposed to 6-benzylaminopurine.Chemosphere. 2019 Oct;233:336-346. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.261. Epub 2019 Jun 1. Chemosphere. 2019. PMID: 31176896
-
Famoxadone-cymoxanil induced cardiotoxicity in zebrafish embryos.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020 Dec 1;205:111339. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111339. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020. PMID: 32961491
-
Molecular programming of the corticosteroid stress axis during zebrafish development.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2009 May;153(1):49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.12.008. Epub 2008 Dec 25. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19146973 Review.
-
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Hypofunction in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME)/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) as a Consequence of Activated Immune-Inflammatory and Oxidative and Nitrosative Pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Nov;54(9):6806-6819. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0170-2. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27766535 Review.
References
-
- NLM PubChem Compound Summary for CID 62389, 6-Benzylaminopurine. [(accessed on 31 March 2022)]; Available online: https://pubchemncbinlmnihgov/compound/6-Benzylaminopurine.
-
- Mi P., Zhang Q.P., Li S.B., Liu X.Y., Zhang S.H., Li M., Chen D.Y., Zhao X., Feng D.F., Feng X.Z. Melatonin protects embryonic development and maintains sleep/wake behaviors from the deleterious effects of fluorene-9-bisphenol in zebrafish (Danio rerio) J. Pineal Res. 2019;66:e12530. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12530. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

