Innovative Treatment Strategies to Accelerate Wound Healing: Trajectory and Recent Advancements
- PMID: 35954282
- PMCID: PMC9367945
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11152439
Innovative Treatment Strategies to Accelerate Wound Healing: Trajectory and Recent Advancements
Abstract
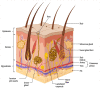
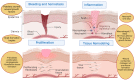
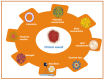
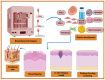
Wound healing is highly specialized dynamic multiple phase process for the repair of damaged/injured tissues through an intricate mechanism. Any failure in the normal wound healing process results in abnormal scar formation, and chronic state which is more susceptible to infections. Chronic wounds affect patients' quality of life along with increased morbidity and mortality and are huge financial burden to healthcare systems worldwide, and thus requires specialized biomedical intensive treatment for its management. The clinical assessment and management of chronic wounds remains challenging despite the development of various therapeutic regimens owing to its painstakingly long-term treatment requirement and complex wound healing mechanism. Various conventional approaches such as cell therapy, gene therapy, growth factor delivery, wound dressings, and skin grafts etc., are being utilized for promoting wound healing in different types of wounds. However, all these abovementioned therapies are not satisfactory for all wound types, therefore, there is an urgent demand for the development of competitive therapies. Therefore, there is a pertinent requirement to develop newer and innovative treatment modalities for multipart therapeutic regimens for chronic wounds. Recent developments in advanced wound care technology includes nanotherapeutics, stem cells therapy, bioengineered skin grafts, and 3D bioprinting-based strategies for improving therapeutic outcomes with a focus on skin regeneration with minimal side effects. The main objective of this review is to provide an updated overview of progress in therapeutic options in chronic wounds healing and management over the years using next generation innovative approaches. Herein, we have discussed the skin function and anatomy, wounds and wound healing processes, followed by conventional treatment modalities for wound healing and skin regeneration. Furthermore, various emerging and innovative strategies for promoting quality wound healing such as nanotherapeutics, stem cells therapy, 3D bioprinted skin, extracellular matrix-based approaches, platelet-rich plasma-based approaches, and cold plasma treatment therapy have been discussed with their benefits and shortcomings. Finally, challenges of these innovative strategies are reviewed with a note on future prospects.
Keywords: 3D bioprinting; chronic wounds; improved wound management; nanotherapeutics; stem cells; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent advances in molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing and its treatments.Front Immunol. 2024 May 21;15:1395479. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1395479. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38835782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Multifaceted Next-Generation Technologies for Improved Skin Wound Healing.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021 Nov 15;4(11):7738-7763. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.1c00880. Epub 2021 Nov 1. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021. PMID: 35006758 Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Design of Three-Dimensional and Bioprinted Scaffolds for Full-Thickness Wound Healing.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022 Feb;28(1):160-181. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2020.0339. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022. PMID: 33446047 Review.
-
Advanced Dressings for Chronic Wound Management.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 May 20;7(5):2660-2676. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c00138. Epub 2024 May 9. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 38723276 Review.
-
Emerging and innovative approaches for wound healing and skin regeneration: Current status and advances.Biomaterials. 2019 Sep;216:119267. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119267. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 31247480 Review.
Cited by
-
Gelatin-/Alginate-Based Hydrogel Scaffolds Reinforced with TiO2 Nanoparticles for Simultaneous Release of Allantoin, Caffeic Acid, and Quercetin as Multi-Target Wound Therapy Platform.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Mar 7;16(3):372. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16030372. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38543266 Free PMC article.
-
Topical application of a hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel integrated with secretome of human mesenchymal stromal cells for diabetic ulcer repair.Regen Ther. 2024 Jul 27;26:520-532. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.07.008. eCollection 2024 Jun. Regen Ther. 2024. PMID: 39156755 Free PMC article.
-
GEO data mining identifies potential immune-related genes in hypertrophic scar and verities in a rabbit model.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 14;9(7):e17266. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17266. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37455989 Free PMC article.
-
The Real-World Effectiveness and Tolerability of a Soothing Cream Containing the Postbiotic Aquaphilus dolomiae Extract-G2 for Skin Healing.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024 Mar;14(3):697-712. doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01119-x. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 38451421 Free PMC article.
-
Double-modified, thio and methylene ATP analogue facilitates wound healing in vitro and in vivo.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 7;14(1):13148. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63759-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38849425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swanson T., Keast D., Cooper R., Black J., Angel D., Schultz G., Carville K., Fletcher J.J.W.I. Ten top tips: Identification of wound infection in a chronic wound. Wounds Int. 2015;6:22–27.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

