Urinary extracellular vesicles and tubular transport
- PMID: 35945648
- PMCID: PMC10310510
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfac235
Urinary extracellular vesicles and tubular transport
Abstract
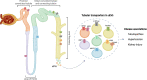
Tubular transport is a key function of the kidney to maintain electrolyte and acid-base homeostasis. Urinary extracellular vesicles (uEVs) harbor water, electrolyte, and acid-base transporters expressed at the apical plasma membrane of tubular epithelial cells. Within the uEV proteome, the correlations between kidney and uEV protein abundances are strongest for tubular transporters. Therefore, uEVs offer a noninvasive approach to probing tubular transport in health and disease. Here, we review how kidney tubular physiology is reflected in uEVs and, conversely, how uEVs may modify tubular transport. Clinically, uEV tubular transporter profiling has been applied to rare diseases, such as inherited tubulopathies, but also to more common conditions, such as hypertension and kidney disease. Although uEVs hold the promise to advance the diagnosis of kidney disease to the molecular level, several biological and technical complexities must still be addressed. The future will tell whether uEV analysis will mainly be a powerful tool to study tubular physiology in humans or whether it will move forward to become a diagnostic bedside test.
Keywords: aldosterone; aquaporin; biomarker; chronic kidney disease; exosomes; hypertension.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles: does cargo reflect tissue?Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2022 Sep 1;31(5):464-470. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000822. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 35894281 Review.
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles as markers to assess kidney sodium transport.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Mar;25(2):67-72. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000192. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26717312 Review.
-
In human nephrectomy specimens, the kidney level of tubular transport proteins does not correlate with their abundance in urinary extracellular vesicles.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Sep 1;317(3):F560-F571. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00242.2019. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31241991
-
Renal extracellular vesicles: from physiology to clinical application.J Physiol. 2016 Oct 15;594(20):5735-5748. doi: 10.1113/JP272182. Epub 2016 May 27. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27104781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nephron mass determines the excretion rate of urinary extracellular vesicles.J Extracell Vesicles. 2022 Jan;11(1):e12181. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12181. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022. PMID: 35064766 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles as a monitoring tool for renal damage in patients not meeting criteria for chronic kidney disease.J Extracell Biol. 2024 Sep 17;3(9):e170. doi: 10.1002/jex2.170. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39290459 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Bench to Bedside?Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 26;13(3):443. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030443. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766548 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

