VND-INTERACTING2 effectively inhibits transcriptional activities of VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN7 through a conserved sequence
- PMID: 35937523
- PMCID: PMC9300430
- DOI: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.22.0122a
VND-INTERACTING2 effectively inhibits transcriptional activities of VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN7 through a conserved sequence
Abstract
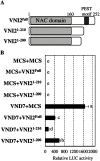
An Arabidopsis NAC domain transcription factor VND-INTERACTING2 (VNI2) was originally isolated as an interacting protein with another NAC domain transcription factor, VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN7 (VND7), a master regulator of xylem vessel element differentiation. VNI2 inhibits transcriptional activation activity of VND7 by forming a protein complex. Here, to obtain insights into how VNI2 regulates VND7, we tried to identify the amino acid region of VNI2 required for inhibition of VND7. VNI2 has an amino acid sequence similar to the ETHYLENE-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT BINDING FACTOR (ERF)-associated amphiphilic repression (EAR) motif, conserved in transcriptional repressors, at the C-terminus. A transient expression assay showed that the EAR-like motif of VNI2 was not required for inhibition of VND7. The C-terminal deletion series of VNI2 revealed that 10 amino acid residues, highly conserved in the VNI2 orthologs contributed to effective repression of the transcriptional activation activity of VND7. Observation of transgenic plants ectopically expressing VNI2 showed that the identified 10 amino acid sequence strongly affected xylem vessel formation and plant growth. These data indicated that the 10 amino acid sequence of VNI2 has an important role in its transcriptional repression activity and negative regulation of xylem vessel formation.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; NAC domain transcription factor; protein-protein interaction; transcriptional repressor; xylem vessel formation.
© 2022 Japanese Society for Plant Biotechnology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
NAC domain transcription factors VNI2 and ATAF2 form protein complexes and regulate leaf senescence.Plant Direct. 2023 Sep 18;7(9):e529. doi: 10.1002/pld3.529. eCollection 2023 Sep. Plant Direct. 2023. PMID: 37731912 Free PMC article.
-
An Arabidopsis NAC domain transcriptional activator VND7 negatively regulates VNI2 expression.Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2021 Dec 25;38(4):415-420. doi: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.21.1013a. Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 35087306 Free PMC article.
-
VND-INTERACTING2, a NAC domain transcription factor, negatively regulates xylem vessel formation in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2010 Apr;22(4):1249-63. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.064048. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 20388856 Free PMC article.
-
Xylem vessel cell differentiation: A best model for new integrative cell biology?Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2021 Dec;64:102135. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2021.102135. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34768235 Review.
-
Lend Me Your EARs: A Systematic Review of the Broad Functions of EAR Motif-Containing Transcriptional Repressors in Plants.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;14(2):270. doi: 10.3390/genes14020270. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NAC domain transcription factors VNI2 and ATAF2 form protein complexes and regulate leaf senescence.Plant Direct. 2023 Sep 18;7(9):e529. doi: 10.1002/pld3.529. eCollection 2023 Sep. Plant Direct. 2023. PMID: 37731912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asahina M, Azuma K, Pitaksaringkarn W, Yamazaki T, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M, Yamaguchi S, Kamiya Y, Okada K, Nishimura T, et al. (2011) Spatially selective hormonal control of RAP2.6L and ANAC071 transcription factors involved in tissue reunion in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 16128–16132 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duval M, Hsieh TF, Kim SY, Thomas TL (2002) Molecular characterization of AtNAM: A member of the Arabidopsis NAC domain superfamily. Plant Mol Biol 50: 237–248 - PubMed
-
- Endo H, Yamaguchi M, Tamura T, Nakano Y, Nishikubo N, Yoneda A, Kato K, Kubo M, Kajita S, Katayama Y, et al. (2015) Multiple classes of transcription factors regulate the expression of VASCULAR-RELATED NAC-DOMAIN7, a master switch of xylem vessel differentiation. Plant Cell Physiol 56: 242–254 - PubMed
-
- Hiratsu K, Matsui K, Koyama T, Ohme-Takagi M (2003) Dominant repression of target genes by chimeric repressors that include the EAR motif, a repression domain, in Arabidopsis. Plant J 34: 733–739 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
