Inositol hexakisphosphate kinases differentially regulate trafficking of vesicular glutamate transporters 1 and 2
- PMID: 35936490
- PMCID: PMC9355605
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.926794
Inositol hexakisphosphate kinases differentially regulate trafficking of vesicular glutamate transporters 1 and 2
Abstract
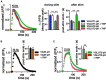
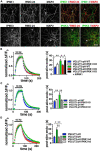
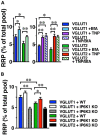
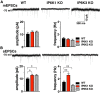
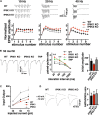
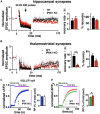
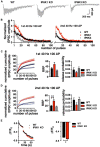
Inositol pyrophosphates have been implicated in cellular signaling and membrane trafficking, including synaptic vesicle (SV) recycling. Inositol hexakisphosphate kinases (IP6Ks) and their product, diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate (PP-IP5 or IP7), directly and indirectly regulate proteins important in vesicle recycling by the activity-dependent bulk endocytosis pathway (ADBE). In the present study, we show that two isoforms, IP6K1 and IP6K3, are expressed in axons. The role of the kinases in SV recycling are investigated using pharmacologic inhibition, shRNA knockdown, and IP6K1 and IP6K3 knockout mice. Live-cell imaging experiments use optical reporters of SV recycling based on vesicular glutamate transporter isoforms, VGLUT1- and VGLUT2-pHluorins (pH), which recycle differently. VGLUT1-pH recycles by classical AP-2 dependent endocytosis under moderate stimulation conditions, while VGLUT2-pH recycles using AP-1 and AP-3 adaptor proteins as well. Using a short stimulus to release the readily releasable pool (RRP), we show that IP6K1 KO increases exocytosis of both VGLUT1-and VGLUT2-pH, while IP6K3 KO decreases the amount of both transporters in the RRP. In electrophysiological experiments we measure glutamate signaling with short stimuli and under the intense stimulation conditions that trigger bulk endocytosis. IP6K1 KO increases synaptic facilitation and IP6K3 KO decreases facilitation compared to wild type in CA1 hippocampal Schaffer collateral synapses. After intense stimulation, the rate of endocytosis of VGLUT2-pH, but not VGLUT1-pH, is increased by knockout, knockdown, and pharmacologic inhibition of IP6Ks. Thus IP6Ks differentially affect the endocytosis of two SV protein cargos that use different endocytic pathways. However, while IP6K1 KO and IP6K3 KO exert similar effects on endocytosis after stimulation, the isoforms exert different effects on exocytosis earlier in the stimulus and on the early phase of glutamate release. Taken together, the data indicate a role for IP6Ks both in exocytosis early in the stimulation period and in endocytosis, particularly under conditions that may utilize AP-1/3 adaptors.
Keywords: endocytosis; exocytosis; inositol hexakisphosphate kinase (IP6K); synaptic vesicle; vesicular glutamate transporter.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Datunashvili, Reyes and Voglmaier.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Inositol Hexakisphosphate Kinase in the Central Nervous System.Biomolecules. 2023 Aug 28;13(9):1317. doi: 10.3390/biom13091317. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VGLUT2 Trafficking Is Differentially Regulated by Adaptor Proteins AP-1 and AP-3.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Oct 26;11:324. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00324. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29123471 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol Pyrophosphate Metabolism Regulates Presynaptic Vesicle Cycling at Central Synapses.iScience. 2020 Apr 24;23(4):101000. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101000. Epub 2020 Mar 22. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32252022 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol Hexakisphosphate Kinase-3 Regulates the Morphology and Synapse Formation of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells via Spectrin/Adducin.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 5;35(31):11056-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1069-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26245967 Free PMC article.
-
The Key Role of IP6K: A Novel Target for Anticancer Treatments?Molecules. 2020 Sep 25;25(19):4401. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194401. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32992691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precise CRISPR-Cas9-mediated mutation of a membrane trafficking domain in the Drosophila vesicular monoamine transporter gene.Curr Res Physiol. 2023 Jun 20;6:100101. doi: 10.1016/j.crphys.2023.100101. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37409154 Free PMC article.
-
pOpsicle: An all-optical reporter system for synaptic vesicle recycling combining pH-sensitive fluorescent proteins with optogenetic manipulation of neuronal activity.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Mar 31;17:1120651. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1120651. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37066081 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping the Future of Obesity Treatment: In Silico Multi-Modeling of IP6K1 Inhibitors for Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunction.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 19;17(2):263. doi: 10.3390/ph17020263. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399478 Free PMC article.
-
Deleting IP6K1 stabilizes neuronal sodium-potassium pumps and suppresses excitability.Mol Brain. 2024 Feb 13;17(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13041-024-01080-y. Mol Brain. 2024. PMID: 38350944 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Inositol Hexakisphosphate Kinase in the Central Nervous System.Biomolecules. 2023 Aug 28;13(9):1317. doi: 10.3390/biom13091317. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37759717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

