Cell secretomes for wound healing and tissue regeneration: Next generation acellular based tissue engineered products
- PMID: 35923177
- PMCID: PMC9340325
- DOI: 10.1177/20417314221114273
Cell secretomes for wound healing and tissue regeneration: Next generation acellular based tissue engineered products
Abstract
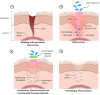
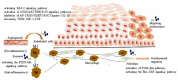
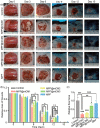
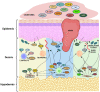
Wound represents a significant socioeconomic burden for both affected individuals and as a whole healthcare system. Accordingly, stem cells have garnered attention due to their differentiation capacity and ability to aid tissue regeneration by releasing biologically active molecules, found in the cells' cultivated medium which known as conditioned medium (CM) or secretomes. This acellular approach provides a huge advantage over conventional treatment options, which are mainly used cellular treatment at wound closure. Interestingly, the secretomes contained the cell-secreted proteins such as growth factors, cytokines, chemokines, extracellular matrix (ECM), and small molecules including metabolites, microvesicles, and exosomes. This review aims to provide a general view on secretomes and how it is proven to have great potential in accelerating wound healing. Utilizing the use of secretomes with its secreted proteins and suitable biomaterials for fabrications of acellular skin substitutes can be promising in treating skin loss and accelerate the healing process.
Keywords: Secretomes; conditioned medium; secreted protein; tissue regeneration; wound healing.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived secretomes-enriched alginate/ extracellular matrix hydrogel patch accelerates skin wound healing.Biomater Res. 2023 Oct 31;27(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s40824-023-00446-y. Biomater Res. 2023. PMID: 37904231 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of secretomes derived from human dermal and adipose tissue mesenchymal stem/stromal cells for skin wound healing: not as effective as cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jan 17;15(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03630-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38229157 Free PMC article.
-
An Exosome-Rich Conditioned Medium from Human Amniotic Membrane Stem Cells Facilitates Wound Healing via Increased Reepithelization, Collagen Synthesis, and Angiogenesis.Cells. 2023 Nov 24;12(23):2698. doi: 10.3390/cells12232698. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067126 Free PMC article.
-
Secretomes as an emerging class of bioactive ingredients for enhanced cosmeceutical applications.Exp Dermatol. 2022 May;31(5):674-688. doi: 10.1111/exd.14570. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Exp Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35338666 Review.
-
Functionalised-biomatrix for wound healing and cutaneous regeneration: future impactful medical products in clinical translation and precision medicine.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 May 24;11:1160577. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1160577. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37292094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Light-triggered protease-mediated release of actin-bound cargo from synthetic cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 15:2024.09.15.613133. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.15.613133. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39314483 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A bibliometric analysis of hotpots and trends for the relationship between skin inflammation and regeneration.Front Surg. 2023 Apr 21;10:1180624. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2023.1180624. eCollection 2023. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 37151861 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Safety Assessments of High-Purified Ovine Collagen Type I Biomatrix for Future Therapeutic Product: International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) Settings.Polymers (Basel). 2023 May 24;15(11):2436. doi: 10.3390/polym15112436. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37299233 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Wound-Healing Products Based on Natural Compounds, Stem Cells, and MicroRNA-Based Biopolymers in the European, USA, and Asian Markets: Opportunities, Barriers, and Regulatory Issues.Polymers (Basel). 2024 May 3;16(9):1280. doi: 10.3390/polym16091280. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38732749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell secretome promotes skin regeneration and rejuvenation: From mechanism to therapeutics.Cell Prolif. 2024 Apr;57(4):e13586. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13586. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38148579 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shin H, Ryu HH, Kwon O, et al.. Clinical use of conditioned media of adipose tissue-derived stem cells in female pattern hair loss: a retrospective case series study. Int J Dermatol 2015; 54: 730–735. - PubMed
-
- Noverina R, Widowati W, Ayuningtyas W, et al.. Growth factors profile in conditioned medium human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (CM-hATMSCs). Clin Nutr Exp 2019; 24: 34–44.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

