FGD1 Variant Associated With Aarskog-Scott Syndrome
- PMID: 35911831
- PMCID: PMC9329920
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.888923
FGD1 Variant Associated With Aarskog-Scott Syndrome
Abstract
Background: Aarskog-Scott syndrome, a rare X-linked genetic disorder, is identified by combined clinical manifestations of short stature, facial, skeletal, and genital anomalies. Annually, two or three new cases are diagnosed with Aarskog-Scott syndrome, which is associated with FGD1 variants. However, there is no specific treatment for Aarskog-Scott syndrome due to its unclear mechanism.
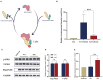
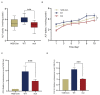
Methods: Clinical data were collected when the patient first visited the hospital. Trio whole-exome sequencing and Sanger sequencing were performed for the genetic cause of disease. To evaluate the pathogenicity of the variants in vitro, stable cell lines were constructed using lentivirus infection in 143B cell. Furthermore, Western blot was used to verify the expression of signaling pathway-related proteins, and the transcription levels of osteogenic-related genes were verified by luciferase reporter gene assay.
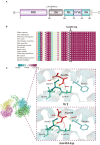
Results: A 7-year-old boy was manifested with facial abnormalities, intellectual disability, and short stature (-3.98 SDS) while the growth hormone level of stimulation test was normal. Trio whole-exome sequencing and Sanger sequencing identified a variant (c.1270A>G, p.Asn424Asp) in FGD1 gene. The Asn424 residue was highly conserved and the hydrogen bond in the FGD1 variant protein has changed, which led to decrease in the interaction with CDC42 protein. In vitro study showed that the Asn424Asp variant significantly decreased the transcription levels of OCN, COL1A1, and ALP activity, and it activated the phosphorylation of JNK1.
Conclusion: Molecular biological mechanisms between abnormal expression of FGD1and Aarskog-Scott syndrome remain poorly understood. In our study, c.1270A>G variant of FGD1 resulted in Aarskog-Scott syndrome, and the analysis of pathogenicity supports the deleterious effect of the variant. Furthermore, we demonstrated the weakened affinity of the mutant FGD1 and CDC42. Decreased expression of osteogenic-related gene and abnormal activation of JNK1 were also shown in this work.
Keywords: Aarskog-Scott syndrome; CDC42; FGD1; JNK1; short stature.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Chen, Lin, Lu, Qu, Yan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FGD1-related Aarskog-Scott syndrome: Identification of four novel variations and a literature review of clinical and molecular aspects.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 May;183(5):2257-2272. doi: 10.1007/s00431-024-05484-9. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38411716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Report: Aarskog-scott syndrome caused by FGD1 gene variation: A family study.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 16;13:932073. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.932073. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36051692 Free PMC article.
-
Novel variant in the FGD1 gene causing Aarskog-Scott syndrome.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Jun;13(6):2623-2628. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4301. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28587322 Free PMC article.
-
A novel frameshift mutation in the FGD1 gene causing Aarskog-Scott syndrome patient with hypogonadism: a case report.Transl Pediatr. 2021 May;10(5):1377-1385. doi: 10.21037/tp-21-26. Transl Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34189097 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: Role of genetic changes of faciogenital dysplasia protein 1 in human disease.Physiol Genomics. 2016 Jul 1;48(7):446-54. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00101.2015. Epub 2016 May 6. Physiol Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27199457 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

