Transient upregulation of EGR1 signaling enhances kidney repair by activating SOX9+ renal tubular cells
- PMID: 35910788
- PMCID: PMC9330523
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.73426
Transient upregulation of EGR1 signaling enhances kidney repair by activating SOX9+ renal tubular cells
Abstract
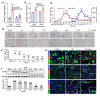
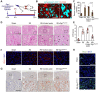
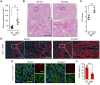
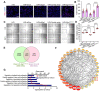
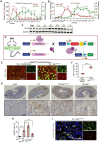
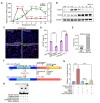
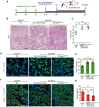
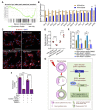
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with damage to the nephrons and tubular epithelial cells (TECs), which can lead to chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Identifying new biomarkers before kidney dysfunction will offer crucial insight into preventive and therapeutic options for the treatment of AKI. Early growth response 1 (EGR1) has been found to be a pioneer transcription factor that can sequentially turn on/off key downstream genes to regulate whole-body regeneration processes in the leopard worm. Whether EGR1 modulates renal regeneration processes in AKI remains to be elucidated. Methods: AKI models of ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) and folic acid (FA) were developed to investigate the roles of EGR1 in kidney injury and regeneration. To further determine the function of EGR1, Egr1-/- mice were applied. Furthermore, RNA sequencing of renal TECs, Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay, and Dual-luciferase reporter assay were carried out to investigate whether EGR1 affects the expression of SOX9. Results: EGR1 is highly expressed in the kidney after AKI both in humans and mice through analysis of the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Furthermore, we verified that EGR1 rapidly up-regulates in the very early stage of IRI and nephrotoxic models of AKI, and validation studies confirmed the essential roles of EGR1 in renal tubular cell regeneration. Further experiments affirmed that genetic inhibition of Egr1 aggravates the severity of AKI in mouse models. Furthermore, our results revealed that EGR1 could increase SOX9 expression in renal TECs by directly binding to the promoter of the Sox9 gene, thus promoting SOX9+ cell proliferation by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Conclusions: Together, our results demonstrated that rapid and transient induction of EGR1 plays a renoprotective role in AKI, which highlights the prospects of using EGR1 as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury (AKI); Early growth response 1 (EGR1); Regeneration; SOX9; Tubular epithelial cells (TECs).
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autophagy activates EGR1 via MAPK/ERK to induce FGF2 in renal tubular cells for fibroblast activation and fibrosis during maladaptive kidney repair.Autophagy. 2024 May;20(5):1032-1053. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2281156. Epub 2023 Nov 18. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 37978868 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9 promotes stress-responsive transcription of VGF nerve growth factor inducible gene in renal tubular epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2020 Nov 27;295(48):16328-16341. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015110. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32887795 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc finger protein 24-dependent transcription factor SOX9 up-regulation protects tubular epithelial cells during acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2023 Jun;103(6):1093-1104. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.02.026. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Kidney Int. 2023. PMID: 36921719 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of macrophage polarization and interaction with renal tubular epithelial cells in ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022 Feb 25;74(1):28-38. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35199123 Review. Chinese.
-
Metabolic Flexibility and Innate Immunity in Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury: The Fine Balance Between Adaptive Repair and Tissue Degeneration.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 7;11:1346. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01346. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32733450 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of ferroptosis-related genes in renal ischemia reperfusion and evaluate the potential impact on kidney transplantation.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 6;15:1394477. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1394477. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39308866 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of ferroptosis reverses heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in mice.J Transl Med. 2024 Feb 24;22(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04734-y. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38402404 Free PMC article.
-
Activated SOX9+ renal epithelial cells promote kidney repair through secreting factors.Cell Prolif. 2023 Apr;56(4):e13394. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13394. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36601693 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk among proximal tubular cells, macrophages, and fibroblasts in acute kidney injury: single-cell profiling from the perspective of ferroptosis.Hum Cell. 2024 Jul;37(4):1039-1055. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01072-z. Epub 2024 May 16. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 38753279 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive Potential of Pistacia lentiscus var. Chia: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Implications.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 5;16(13):2152. doi: 10.3390/nu16132152. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet. 2012;380:756–66. - PubMed
-
- Han Q, Ai S, Hong Q, Zhang C, Song Y, Wang X. et al. A supramolecular hydrogel based on the combination of YIGSR and RGD enhances mesenchymal stem cells paracrine function via integrin α2β1 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway for acute kidney injury therapy. Chem Eng J. 2022;436:135088.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

