Quorum Quenching-Guided Inhibition of Mixed Bacterial Biofilms and Virulence Properties by Protein Derived From Leaves of Carissa carandas
- PMID: 35909977
- PMCID: PMC9329584
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.836819
Quorum Quenching-Guided Inhibition of Mixed Bacterial Biofilms and Virulence Properties by Protein Derived From Leaves of Carissa carandas
Abstract
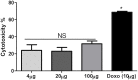
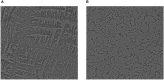
The inhibition/degradation potential of Carissa carandas proteinaceous leaf extract against mixed bacterial biofilm of Staphylococcus aureus MTCC 96, Escherichia coli MTCC 1304, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 741, and Klebsiella pneumoniae MTCC 109, responsible for nosocomial infections, was evaluated. Distinct inhibition/degradation of mixed bacterial biofilm by the proteinaceous leaf extract of C. carandas was observed under a microscope, and it was found to be 80%. For mono-species biofilm, the maximum degradation of 70% was observed against S. aureus biofilm. The efficiency of aqueous plant extracts to inhibit the mono-species biofilm was observed in terms of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), and the best was found against P. aeruginosa (12.5 μg/ml). The presence of flavonoids, phenols, and tannins in the phytochemical analysis of the plant extract suggests the main reason for the antibiofilm property of C. carandas. From the aqueous extract, protein fraction was precipitated using 70% ammonium sulfate and dialyzed. This fraction was purified by ion-exchange chromatography and found to be stable and active at 10°C (pH 7). The purified fraction showed less than 40% cytotoxicity, which suggests that it can be explored for therapeutic purposes after in-depth testing. In order to investigate the mechanistic action of the biofilm inhibition, the plant protein was tested against Chromobacterium violaceum CV026, and its inhibitory effect confirmed its quorum quenching nature. Based on these experimental analyses, it can be speculated that the isolated plant protein might influence the signaling molecule that leads to the inhibition effect of the mixed bacterial biofilm. Further experimental studies are warranted to validate our current findings.
Keywords: biofilm; nosocomial infection; quorum quenching; quorum sensing; virulence.
Copyright © 2022 Shukla, Singh, Habeeballah, Alkhanani, Lata, Hussain, Mukherjee, Pasupuleti, Meena, Mishra and Haque.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of biofilm and quorum sensing-regulated virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Cuphea carthagenensis (Jacq.) J. F. Macbr. Leaf extract: An in vitro study.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113699. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113699. Epub 2020 Dec 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33340600
-
A medicinal herb Cassia alata attenuates quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017 Mar;64(3):231-238. doi: 10.1111/lam.12710. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28035685
-
Anti-quorum Sensing and Anti-biofilm Activity of Delftia tsuruhatensis Extract by Attenuating the Quorum Sensing-Controlled Virulence Factor Production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jul 26;7:337. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00337. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28798903 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving biofilm inhibition and eradication in clinical settings through plant-based antibiofilm agents.Phytomedicine. 2023 Oct;119:154973. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154973. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37499434 Review.
-
Quorum sensing inhibition and antibiofilm action of triterpenoids: An updated insight.Fitoterapia. 2023 Jun;167:105508. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2023.105508. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Fitoterapia. 2023. PMID: 37059209 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

