Modular safe-harbor transgene insertion for targeted single-copy and extrachromosomal array integration in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 35900171
- PMCID: PMC9434227
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac184
Modular safe-harbor transgene insertion for targeted single-copy and extrachromosomal array integration in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
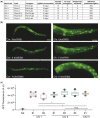
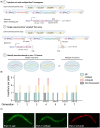
Efficient and reproducible transgenesis facilitates and accelerates research using genetic model organisms. Here, we describe a modular safe-harbor transgene insertion (MosTI) for use in Caenorhabditis elegans which improves targeted insertion of single-copy transgenes by homology directed repair and targeted integration of extrachromosomal arrays by nonhomologous end-joining. MosTI allows easy conversion between selection markers at insertion site and a collection of universal targeting vectors with commonly used promoters and fluorophores. Insertions are targeted at three permissive safe-harbor intergenic locations and transgenes are reproducibly expressed in somatic and germ cells. Chromosomal integration is mediated by CRISPR/Cas9, and positive selection is based on a set of split markers (unc-119, hygroR, and gfp) where only animals with chromosomal insertions are rescued, resistant to antibiotics, or fluorescent, respectively. Single-copy insertion is efficient using either constitutive or heat-shock inducible Cas9 expression (25-75%) and insertions can be generated from a multiplexed injection mix. Extrachromosomal array integration is also efficient (7-44%) at modular safe-harbor transgene insertion landing sites or at the endogenous unc-119 locus. We use short-read sequencing to estimate the plasmid copy numbers for 8 integrated arrays (6-37 copies) and long-read Nanopore sequencing to determine the structure and size (5.4 Mb) of 1 array. Using universal targeting vectors, standardized insertion strains, and optimized protocols, it is possible to construct complex transgenic strains which should facilitate the study of increasingly complex biological problems in C. elegans.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; CRISPR/Cas9; genome engineering; long-read assembly; transgenesis.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America.
Figures




Similar articles
-
High-throughput library transgenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans via Transgenic Arrays Resulting in Diversity of Integrated Sequences (TARDIS).Elife. 2023 Jul 4;12:RP84831. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84831. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37401921 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Self-Selecting and Clone-Free Integration of Transgenes into Engineered CRISPR Safe Harbor Locations in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Oct 5;10(10):3775-3782. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401400. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32816924 Free PMC article.
-
Creation of low-copy integrated transgenic lines in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2001 Mar;157(3):1217-26. doi: 10.1093/genetics/157.3.1217. Genetics. 2001. PMID: 11238406 Free PMC article.
-
The application of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Genet Genomics. 2015 Aug 20;42(8):413-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 26. J Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26336798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenesis in C. elegans.Methods Cell Biol. 2011;106:161-85. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-544172-8.00006-2. Methods Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 22118277 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing short germline-specific promoters with a range of expression levels in C. elegans.MicroPubl Biol. 2023 Jul 10;2023:10.17912/micropub.biology.000843. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000843. eCollection 2023. MicroPubl Biol. 2023. PMID: 37497182 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput library transgenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans via Transgenic Arrays Resulting in Diversity of Integrated Sequences (TARDIS).Elife. 2023 Jul 4;12:RP84831. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84831. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37401921 Free PMC article.
-
A cGAL-UAS bipartite expression toolkit for Caenorhabditis elegans sensory neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 19;120(51):e2221680120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221680120. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38096407 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and inherited piRNA-mediated silencing in a rde-3 ribonucleotidyltransferase mutant.MicroPubl Biol. 2022 Sep 14;2022:10.17912/micropub.biology.000638. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000638. eCollection 2022. MicroPubl Biol. 2022. PMID: 36188099 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted insertion and reporter transgene activity at a gene safe harbor of the human blood fluke, Schistosoma mansoni.Cell Rep Methods. 2023 Jul 24;3(7):100535. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100535. eCollection 2023 Jul 24. Cell Rep Methods. 2023. PMID: 37533651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; 2010. https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
