Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals the Prognostic Potential of the THAP9/THAP9-AS1 Sense-Antisense Gene Pair in Human Cancers
- PMID: 35893234
- PMCID: PMC9326536
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna8040051
Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals the Prognostic Potential of the THAP9/THAP9-AS1 Sense-Antisense Gene Pair in Human Cancers
Abstract
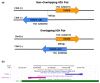
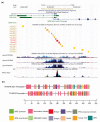
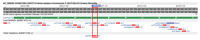
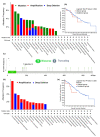
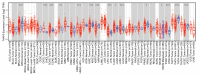
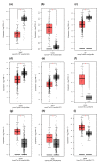
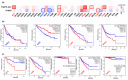
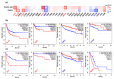
Human THAP9, which encodes a domesticated transposase of unknown function, and lncRNA THAP9-AS1 (THAP9-antisense1) are arranged head-to-head on opposite DNA strands, forming a sense and antisense gene pair. We predict that there is a bidirectional promoter that potentially regulates the expression of THAP9 and THAP9-AS1. Although both THAP9 and THAP9-AS1 are reported to be involved in various cancers, their correlative roles on each other's expression has not been explored. We analyzed the expression levels, prognosis, and predicted biological functions of the two genes across different cancer datasets (TCGA, GTEx). We observed that although the expression levels of the two genes, THAP9 and THAP9-AS1, varied in different tumors, the expression of the gene pair was strongly correlated with patient prognosis; higher expression of the gene pair was usually linked to poor overall and disease-free survival. Thus, THAP9 and THAP9-AS1 may serve as potential clinical biomarkers of tumor prognosis. Further, we performed a gene co-expression analysis (using WGCNA) followed by a differential gene correlation analysis (DGCA) across 22 cancers to identify genes that share the expression pattern of THAP9 and THAP9-AS1. Interestingly, in both normal and cancer samples, THAP9 and THAP9-AS1 often co-express; moreover, their expression is positively correlated in each cancer type, suggesting the coordinated regulation of this H2H gene pair.
Keywords: TCGA; THAP9; THAP9-AS1; co-expression; guilt-by-association; head-to-head genes; pan-cancer; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
LncRNA THAP9-AS1 highly expressed in tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma and accelerates tumor cell proliferation.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec;46(10):102025. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2022.102025. Epub 2022 Sep 25. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36170961
-
THAP9-AS1/miR-133b/SOX4 positive feedback loop facilitates the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Apr 14;12(4):401. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03690-z. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33854048 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA THAP9-AS1 Promotes Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Growth and Leads to a Poor Clinical Outcome via Sponging miR-484 and Interacting with YAP.Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Apr 1;26(7):1736-1748. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0674. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31831555
-
The role of long non-coding RNA AFAP1-AS1 in human malignant tumors.Pathol Res Pract. 2018 Oct;214(10):1524-1531. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.08.014. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Pathol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30173945 Review.
-
DARS-AS1: A Vital Oncogenic LncRNA Regulator with Potential for Cancer Prognosis and Therapy.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Jan 20;21(3):571-582. doi: 10.7150/ijms.90611. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38322590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

