IgG Fusion Proteins for Brain Delivery of Biologics via Blood-Brain Barrier Receptor-Mediated Transport
- PMID: 35890374
- PMCID: PMC9322584
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071476
IgG Fusion Proteins for Brain Delivery of Biologics via Blood-Brain Barrier Receptor-Mediated Transport
Abstract
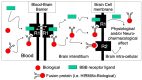
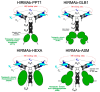
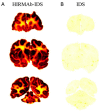
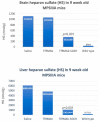
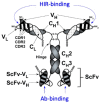
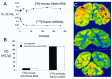
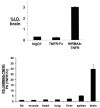
The treatment of neurological disorders with large-molecule biotherapeutics requires that the therapeutic drug be transported across the blood-brain barrier (BBB). However, recombinant biotherapeutics, such as neurotrophins, enzymes, decoy receptors, and monoclonal antibodies (MAb), do not cross the BBB. These biotherapeutics can be re-engineered as brain-penetrating bifunctional IgG fusion proteins. These recombinant proteins comprise two domains, the transport domain and the therapeutic domain, respectively. The transport domain is an MAb that acts as a molecular Trojan horse by targeting a BBB-specific endogenous receptor that induces receptor-mediated transcytosis into the brain, such as the human insulin receptor (HIR) or the transferrin receptor (TfR). The therapeutic domain of the IgG fusion protein exerts its pharmacological effect in the brain once across the BBB. A generation of bifunctional IgG fusion proteins has been engineered using genetically engineered MAbs directed to either the BBB HIR or TfR as the transport domain. These IgG fusion proteins were validated in animal models of lysosomal storage disorders; acute brain conditions, such as stroke; or chronic neurodegeneration, such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. Human phase I-III clinical trials were also completed for Hurler MPSI and Hunter MPSII using brain-penetrating IgG-iduronidase and -iduronate-2-sulfatase fusion protein, respectively.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; blood–brain barrier; decoy receptors; fusion proteins; insulin receptor; lysosomal storage disorders; monoclonal antibody; neurotrophic factors; protein-based therapy; transferrin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The author is the co-inventor of patents on the delivery of biological drugs to the brain.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blood-brain barrier drug delivery of IgG fusion proteins with a transferrin receptor monoclonal antibody.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015 Feb;12(2):207-22. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.952627. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 25138991 Review.
-
Reengineering biopharmaceuticals for targeted delivery across the blood-brain barrier.Methods Enzymol. 2012;503:269-92. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396962-0.00011-2. Methods Enzymol. 2012. PMID: 22230573 Review.
-
Delivery of Biologics Across the Blood-Brain Barrier with Molecular Trojan Horse Technology.BioDrugs. 2017 Dec;31(6):503-519. doi: 10.1007/s40259-017-0248-z. BioDrugs. 2017. PMID: 29067674 Review.
-
Treatment of Parkinson's disease with biologics that penetrate the blood-brain barrier via receptor-mediated transport.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Nov 13;15:1276376. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1276376. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38035276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood-brain barrier delivery for lysosomal storage disorders with IgG-lysosomal enzyme fusion proteins.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 May;184:114234. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114234. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35307484 Review.
Cited by
-
The Glycocalyx: The Importance of Sugar Coating the Blood-Brain Barrier.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8404. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158404. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treating late-onset Tay Sachs disease: Brain delivery with a dual trojan horse protein.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Jul 17;32(3):101300. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101300. eCollection 2024 Sep 12. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 39211733 Free PMC article.
-
An update on pathogenesis and clinical scenario for Parkinson's disease: diagnosis and treatment.3 Biotech. 2023 May;13(5):142. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03553-8. Epub 2023 Apr 27. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37124989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-oriented conjugation of poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) for enhanced brain delivery of antibody.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Oct 18;11:1214118. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1214118. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37920826 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies Induced by Environmental Pollutants: Heat Shock Proteins and Proteasome as Promising Therapeutic Tools.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 30;15(8):2048. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082048. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631262 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

