Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells versus Omega n - 3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Gentamicin-Induced Cardiac Degeneration
- PMID: 35890218
- PMCID: PMC9319609
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071322
Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells versus Omega n - 3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Gentamicin-Induced Cardiac Degeneration
Abstract
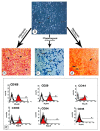
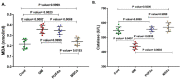
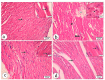
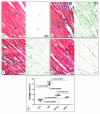
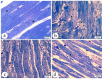
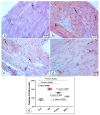
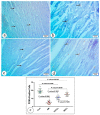
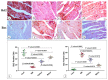
This study compared the cardioprotective action of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and PUFAs in a rat model of gentamicin (GM)-induced cardiac degeneration. Male Wistar albino rats were randomized into four groups of eight rats each: group I (control group), group II (gentamicin-treated rats receiving gentamicin intraperitoneally (IP) at dose of 100 mg/kg/day for 10 consecutive days), group III (gentamicin and PUFA group receiving gentamicin IP at dose of 100 mg/kg/day for 10 consecutive days followed by PUFAs at a dose of 100 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks), and group IV (gentamicin and MSC group receiving gentamicin IP at dose of 100 mg/kg/day followed by a single dose of MSCs (1 × 106)/rat IP). Cardiac histopathology was evaluated via light and electron microscopy. Immunohistochemical detection of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), caspase-3 (apoptosis), Bcl2, and Bax expression was performed. Moreover, cardiac malonaldehyde (MDA) content, catalase activity, and oxidative stress parameters were biochemically evaluated. Light and electron microscopy showed that both MSCs and PUFAs had ameliorative effects. Their actions were mediated by upregulating PCNA expression, downregulating caspase-3 expression, mitigating cardiac MDA content, catalase activity, and oxidative stress parameters. MSCs and PUFAs had ameliorative effects against gentamicin-induced cardiac degeneration, with MSCs showing higher efficacy compared to PUFAs.
Keywords: MDA; PCNA; cardiac degeneration; caspase-3; catalase; mesenchymal stem cells; n − 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic efficacy of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stromal cells versus losartan on adriamycin-induced renal cortical injury in adult albino rats.Cytotherapy. 2016 Aug;18(8):970-984. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.05.004. Cytotherapy. 2016. PMID: 27378342
-
Comparative study of the ameliorative effects of omega-3 versus selenium on etoposide-induced changes in Sertoli cells and ectoplasmic specialization of adult rat testes: immunohistochemical and electron microscopic study.J Mol Histol. 2022 Jun;53(3):523-542. doi: 10.1007/s10735-022-10062-0. Epub 2022 Feb 3. J Mol Histol. 2022. PMID: 35118589
-
Mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with platelet-rich plasma modulate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2019 Jul;38(7):857-874. doi: 10.1177/0960327119842613. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30991846
-
The effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on cardiac rhythm: a critical reassessment.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Oct;140(1):53-80. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 Jun 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23735203 Review.
-
Combined effect of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells and nitric oxide inducer on injured gastric mucosa in a rat model.Tissue Cell. 2016 Dec;48(6):644-652. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2016.09.006. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Tissue Cell. 2016. PMID: 27751517 Review.
Cited by
-
Zamzam Water Ameliorates Gentamicin-Induced Testicular Toxicity in a Rat Model via Targeting Sperm Parameters, Testicular Tissue Oxidative Insult, Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Pituitary-Gonadal Axis.Toxics. 2022 Dec 20;11(1):2. doi: 10.3390/toxics11010002. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36668728 Free PMC article.
-
Potential applications of mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes in regenerative medicine.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023 Jan-Jun;23(6):491-507. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2023.2211203. Epub 2023 May 9. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37147781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kowalewski M., Pawliszak W., Zaborowska K., Navarese E.P., Szwed K.A., Kowalkowska M.E., Kowalewski J., Borkowska A., Anisimowicz L. Gentamicin-collagen sponge reduces the risk of sternal wound infections after heart surgery: Meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015;149:1631–1640.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2015.01.034. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khan Z.A., Hollenberg S.M. Valvular Heart Disease in Adults: Infective Endocarditis. FP Essent. 2017;457:30–38. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

