Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanisms to New Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 35884398
- PMCID: PMC9320011
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14143337
Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Mechanisms to New Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
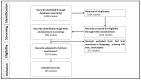
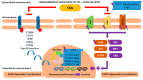
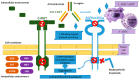
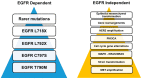
Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in advanced mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) constitutes a therapeutic challenge. This review intends to summarize the existing knowledge about the mechanisms of resistance to TKIs in the context of EGFR mutant NSCLC and discuss its clinical and therapeutic implications. EGFR-dependent and independent molecular pathways have the potential to overcome or circumvent the activity of EGFR-targeted agents including the third-generation TKI, osimertinib, negatively impacting clinical outcomes. CNS metastases occur frequently in patients on EGFR-TKIs, due to the inability of first and second-generation agents to overcome both the BBB and the acquired resistance of cancer cells in the CNS. Newer-generation TKIs, TKIs targeting EGFR-independent resistance mechanisms, bispecific antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates or combinations of TKIs with other TKIs or chemotherapy, immunotherapy and Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors (anti-VEGFs) are currently in use or under investigation in EGFR mutant NSCLC. Liquid biopsies detecting mutant cell-free DNA (cfDNA) provide a window of opportunity to attack mutant clones before they become clinically apparent. Overall, EGFR TKIs-resistant NSCLC constitutes a multifaceted therapeutic challenge. Mapping its underlying mutational landscape, accelerating the detection of resistance mechanisms and diversifying treatment strategies are essential for the management of the disease.
Keywords: EGFR; TKIs; immunotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer; osimertinib; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Audit of Molecular Mechanisms of Primary and Secondary Resistance to Various Generations of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Known Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients in a Tertiary Centre.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022 Nov;34(11):e451-e462. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022. PMID: 35810049
-
Therapeutic strategies for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with osimertinib resistance.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Dec 8;15(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01391-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36482474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment strategies and outcomes for patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer resistant to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Focus on novel therapies.Lung Cancer. 2022 Aug;170:41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.05.011. Epub 2022 May 21. Lung Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35714425 Review.
-
Can we define the optimal sequence of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant nonsmall cell lung cancer?Curr Opin Oncol. 2017 Mar;29(2):89-96. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000350. Curr Opin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28085680 Review.
-
Preclinical Models for Acquired Resistance to Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors in NSCLC: Functional Studies and Drug Combinations Used to Overcome Resistance.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 7;12:853501. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.853501. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35463360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting HER3 to overcome EGFR TKI resistance in NSCLC.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 4;14:1332057. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1332057. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38239350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting CDK1 in cancer: mechanisms and implications.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023 Jun 13;7(1):58. doi: 10.1038/s41698-023-00407-7. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37311884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Retreatment in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Previously Exposed to EGFR-TKI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pers Med. 2024 Jul 15;14(7):752. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070752. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39064005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The deubiquitinase USP9X regulates RIT1 protein abundance and oncogenic phenotypes.iScience. 2024 Jul 14;27(8):110499. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110499. eCollection 2024 Aug 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39161959 Free PMC article.
-
LMNA Reduced Acquired Resistance to Erlotinib in NSCLC by Reversing the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the FGFR/MAPK/c-fos Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 31;23(21):13237. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113237. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Passaro A., Janne P.A., Mok T., Peters S. Overcoming therapy resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat. Cancer. 2021;2:377–391. - PubMed
-
- Tsao M.S., Sakurada A., Cutz J.C., Zhu C.Q., Kamel-Reid S., Squire J., Lorimer I., Zhang T., Liu N., Daneshmand M., et al. Erlotinib in lung cancer—Molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:133–144. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd F.A., Rodrigues Pereira J., Ciuleanu T., Tan E.H., Hirsh V., Thongprasert S., Campos D., Maoleekoonpiroj S., Smylie M., Martins R., et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:123–132. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

