Network pharmacology-based analysis and experimental in vitro validation on the mechanism of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. in the treatment for type I allergy
- PMID: 35879791
- PMCID: PMC9317138
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-022-03677-z
Network pharmacology-based analysis and experimental in vitro validation on the mechanism of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. in the treatment for type I allergy
Abstract
Background: The incidence of allergic reaction is increasing year by year, but the specific mechanism is still unclear. Paeonia lactiflora Pall.(PLP) is a traditional Chinese medicine with various pharmacological effects such as anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and immune regulation. Previous studies have shown that PLP has potential anti-allergic activity. However, there is still no comprehensive analysis of the targeted effects and exact molecular mechanisms of the anti-allergic components of PLP. This study aimed to reveal the mechanism of PLP. in the treatment of type I allergy by combining network pharmacological methods and experimental verification.
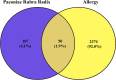
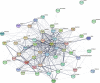
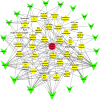
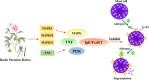
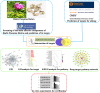
Methods: First, we used the traditional Chinese medicine systems pharmacology (TCMSP) database and analysis platform to screen the main components and targets of PLP, and then used databases such as GeneCards to retrieve target information related to 'allergy'. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis obtained the core target genes in the intersection target, and then imported the intersection target into the David database for gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) analysis. Furthermore, the therapeutic effect of paeoniflorin, the main component of PLP, on IgE-induced type I allergy was evaluated in vitro.
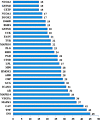
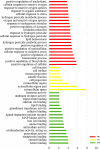
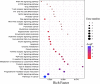
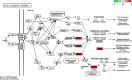
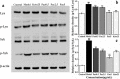
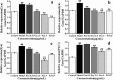
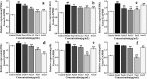
Results: GO analysis obtained the main biological processes, cell components and molecular functions involved in the target genes. KEGG analysis screened out MAPK1, MAPK10, MAPK14 and TNF that have a strong correlation with PLP anti-type I allergy, and showed that PLP may pass through signal pathways such as IgE/FcεR I, PI3K/Akt and MAPK to regulate type I allergy. RT-qPCR and Western Blot results confirmed that paeoniflorin can inhibit the expression of key genes and down-regulate the phosphorylation level of proteins in these signal pathways. It further proved the reliability of the results of network pharmacology research.
Conclusion: The results of this study will provide a basis for revealing the multi-dimensional regulatory mechanism of PLP for the treatment of type I allergy and the development of new drugs.
Keywords: Allergic reaction; IgE/FcεR I; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Mechanism of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium and Paeonia lactiflora herbal pair against liver cancer: an exploration based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jul;47(13):3597-3608. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220110.402. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35850814 Chinese.
-
Study on molecular biological mechanism of Chinese herbal medicines for the treatment of gastric precancerous lesions based on data mining and network pharmacology.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Nov 25;51(5):573-584. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2022-0278. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36581572 Free PMC article. English.
-
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Reveal the Underlying Mechanisms of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. On the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Nov 16;2019:8706589. doi: 10.1155/2019/8706589. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31827565 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
Total glucosides of paeony: A review of its phytochemistry, role in autoimmune diseases, and mechanisms of action.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Aug 10;258:112913. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112913. Epub 2020 May 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32371143 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical analysis, in-vitro and in-silico study of antiproliferative activity of ethyl acetate fraction of Launaea cornuta (Hochst. ex Oliv. & Hiern) C. Jeffrey against human cervical cancer cell line.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 28;15:1399885. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1399885. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39005932 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Allergic and Anti-Inflammatory Signaling Mechanisms of Natural Compounds/Extracts in In Vitro System of RBL-2H3 Cell: A Systematic Review.Cells. 2024 Aug 21;13(16):1389. doi: 10.3390/cells13161389. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39195277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu CX, Liu R, Fan HR, Xiao XF, Chen XP, Xu HY, et al. Network pharmacology bridges traditional application and modern development of traditional Chinese medicine. Chinese Herb Med. 2015;7:3–17. doi: 10.1016/S1674-6384(15)60014-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

