Lymphatic Vascular Permeability
- PMID: 35879102
- PMCID: PMC9380735
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041274
Lymphatic Vascular Permeability
Abstract
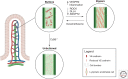
Blood vessels have a regulated permeability to fluid and solutes, which allows for the delivery of nutrients and signaling molecules to all cells in the body, a process essential to life. The lymphatic vasculature is the second network of vessels in the body, making up part of the immune system, yet is not typically thought of as having a permeability to fluid and solute. However, the major function of the lymphatic vasculature is to regulate tissue fluid balance to prevent edema, so lymphatic vessels must be permeable to absorb and transport fluid efficiently. Only recently were lymphatic vessels discovered to be permeable, which has had many functional implications. In this review, we will provide an overview of what is known about lymphatic vascular permeability, discuss the biophysical and signaling mechanisms regulating lymphatic permeability, and examine the disease relevance of this new property of lymphatic vessels.
Copyright © 2022 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
When form meets function: the cells and signals that shape the lymphatic vasculature during development.Development. 2021 Jun 1;148(11):dev167098. doi: 10.1242/dev.167098. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Development. 2021. PMID: 34080610 Review.
-
Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Barrier Dysfunction in Renal Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 23;23(13):6970. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136970. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35805972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular lymphangiogenesis: new players.Trends Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;15(8):434-41. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.06.004. Trends Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16005628 Review.
-
Lymphatic Vascular Permeability Determined from Direct Measurements of Solute Flux.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2711:21-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3429-5_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 37776446
-
Targeted treatment for lymphedema and lymphatic metastasis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1131:215-24. doi: 10.1196/annals.1413.019. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. PMID: 18519974 Review.
Cited by
-
Microvesicles derived from dermal myofibroblasts modify the integrity of the blood and lymphatic barriers using distinct endocytosis pathways.J Extracell Biol. 2024 May 2;3(5):e151. doi: 10.1002/jex2.151. eCollection 2024 May. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38939570 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of lymphatic junctional morphology and the potential effects on cardiovascular diseases.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 28;14:1198052. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1198052. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37187962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Lymphatic Endothelial Cell Junction Transformations.Circ Res. 2023 Aug 4;133(4):350-352. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.323210. Epub 2023 Aug 3. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 37535754 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
