Canine Parainfluenza Virus Infection in a Dog with Acute Respiratory Disease
- PMID: 35878363
- PMCID: PMC9320280
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci9070346
Canine Parainfluenza Virus Infection in a Dog with Acute Respiratory Disease
Abstract
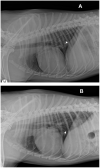
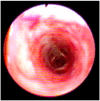
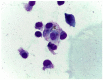
The canine infectious respiratory disease complex (CIRDC) is an endemic respiratory syndrome caused by different bacterial and viral pathogens. This report describes a case of canine parainfluenza virus infection in a vaccinated household dog with an acute respiratory symptom (dry cough), who underwent clinical and endoscopic investigations for a suspected foreign body. Cytological investigations carried out on the broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) tested negative for the presence of inflammatory or infectious processes and could have been misleading the clinicians. By the molecular analyses (PCR) carried out on the BALF, canine parainfluenza virus was exclusively detected without the simultaneous presence of other respiratory pathogens associated to CIRDC. This case report emphasizes the role of molecular diagnostics in the differential diagnosis of respiratory diseases, in order to avoid underestimating the circulation of the parainfluenza virus in the canine population.
Keywords: CIRDC; CPIV; bronchoscopy; dry cough; kennel cough; respiratory syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aetiology of Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease Complex and Prevalence of its Pathogens in Europe.J Comp Pathol. 2020 Apr;176:86-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2020.02.005. Epub 2020 Mar 17. J Comp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32359641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predominance of Canine Parainfluenza Virus and Mycoplasma in Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease Complex in Dogs.Pathogens. 2023 Nov 15;12(11):1356. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111356. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003820 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for canine infectious respiratory disease complex and the pathogens associated with the disease.Can Vet J. 2024 Nov;65(11):1172-1179. Can Vet J. 2024. PMID: 39494180
-
Factors associated with development of Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease Complex (CIRDC) in dogs in 5 Canadian small animal clinics.Can Vet J. 2016 Jan;57(1):46-51. Can Vet J. 2016. PMID: 26740697 Free PMC article.
-
Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease.Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2020 Mar;50(2):405-418. doi: 10.1016/j.cvsm.2019.10.009. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2020. PMID: 31813556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosome-mediated regulation of inflammatory pathway during respiratory viral disease.Virol J. 2024 Jan 25;21(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02297-y. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38273382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Decaro N., Mari V., Larocca V., Losurdo M., Lanave G., Lucente M.S., Corrente M., Catella C., Bo S., Elia G., et al. Molecular surveillance of traditional and emerging pathogens associated with canine infectious respiratory disease. Vet. Microbiol. 2016;192:21–25. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.06.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Greene C.E. Infectious Disease of the Dog and Cat. 4th ed. Elsevier/Saunders; St. Louis, MO, USA: 2012. Nonrespiratory Paramyxovirus Infections of Dogs; p. 66. Chapter 7.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

