Development and Applications of a Zebrafish (Danio rerio) CYP1A-Targeted Monoclonal Antibody (CRC4) with Reactivity across Vertebrate Taxa: Evidence for a Conserved CYP1A Epitope
- PMID: 35878309
- PMCID: PMC9320060
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics10070404
Development and Applications of a Zebrafish (Danio rerio) CYP1A-Targeted Monoclonal Antibody (CRC4) with Reactivity across Vertebrate Taxa: Evidence for a Conserved CYP1A Epitope
Abstract
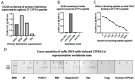
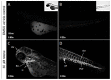
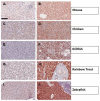
CYP1A is a heme-thiolate enzyme associated with the cytochrome P4501A1 monooxygenase system and is inducible by a wide variety of xenobiotics and endogenous ligands that bind and activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR). The AHR-CYP1A axis is important for detoxification of certain xenobiotics and for homeostatic balance of endogenous sex hormones, amine hormones, vitamins, fatty acids, and phospholipids. Herein, we generated and described applications of a zebrafish CYP1A-targeted monoclonal antibody (mAb CRC4) that fortuitously recognizes induced CYP1A across vertebrate taxa, including fish, chicken, mouse, rat, and human. We then demonstrated that mAb CRC4 targets a highly conserved epitope signature of vertebrate CYP1A. The unique complimentary determining region (CDR) sequences of heavy and light chains were determined, and these Ig sequences will allow for the expression of recombinant mAb CRC4, thus superseding the need for long-term hybridoma maintenance. This antibody works well for immunohistochemistry (IHC), as well as whole-mounted IHC in zebrafish embryos. Monoclonal antibody CRC4 may be particularly useful for studying the AHR-CYP1A axis in multiple vertebrate species and within the context of Oceans and Human Health research. By using archived samples, when possible, we actively promoted efforts to reduce, replace, and refine studies involving live animals.
Keywords: conserved CYP1A epitope; monoclonal antibody (mAb) CRC4; vertebrate CYP1A; whole mount IHC; zebrafish CYP1A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zebrafish cardiotoxicity: the effects of CYP1A inhibition and AHR2 knockdown following exposure to weak aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Jun;22(11):8329-38. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3969-2. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25532870 Free PMC article.
-
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator pathway causes developmental toxicity through a CYP1A-independent mechanism in zebrafish.Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Sep;66(3):512-21. doi: 10.1124/mol.66.3.. Mol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15322242
-
Modification and quantification of in vivo EROD live-imaging with zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos to detect both induction and inhibition of CYP1A.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Feb 15;615:330-347. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.257. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 28982082
-
Biological effects of 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) in vivo are enhanced by loss of CYP1A function in an Ahr2-dependent manner.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 15;110-111:117-29. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.012. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27112072 Free PMC article.
-
Cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A) in teleostean fishes. A review of immunohistochemical studies.Sci Total Environ. 2000 Mar 20;247(2-3):313-32. doi: 10.1016/s0048-9697(99)00500-8. Sci Total Environ. 2000. PMID: 10803558 Review.
Cited by
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent toxicity by retene requires metabolic competence.Toxicol Sci. 2024 Nov 1;202(1):50-68. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfae098. Toxicol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39107868 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk of MAP3K1 and EGFR signaling mediates gene-environment interactions that block developmental tissue closure.J Biol Chem. 2024 Jul;300(7):107486. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107486. Epub 2024 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38897570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Westerfield M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) University of Oregon Press; Eugene, OR, USA: 2007.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

