Characterization of demographic data, clinical signs, comorbidities, and outcomes according to the race in hospitalized individuals with COVID-19 in Brazil: An observational study
- PMID: 35871427
- PMCID: PMC9309002
- DOI: 10.7189/jogh.12.05027
Characterization of demographic data, clinical signs, comorbidities, and outcomes according to the race in hospitalized individuals with COVID-19 in Brazil: An observational study
Abstract
Background: Brazil is a multiracial country with five major official races: White, Black, individuals with multiracial backgrounds, Asian, and Indigenous. Brazil is also one of the epicentres of the Coronavirus Disease (COVID)-19 pandemic. Thus, we evaluated how the races of the Brazilian population contribute to the outcomes in hospitalized individuals with COVID-19, and we also described the clinical profile of the five official Brazilian races.
Methods: We performed an epidemiological analysis for the first 67 epidemiological weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil (from February 22, 2020, to April 04, 2021) using the data available at OpenDataSUS of the Brazilian Ministry of Health, a data set containing data from Brazilian hospitalized individuals. We evaluated more than 30 characteristics, including demographic data, clinical symptoms, comorbidities, need for intensive care unit and mechanical ventilation, and outcomes.
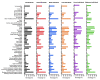
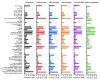
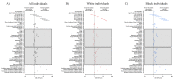
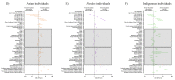
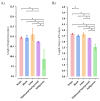
Results: In our data, 585 655 hospitalized individuals with a positive result in SARS-CoV-2 real-time chain reaction (RT-PCR) were included. Of these total, 309 646 (52.9%) identified as White, 31 872 (5.4%) identified as Black, 7108 (1.2%) identified as Asian, 235 108 (40.1%) identified as individuals with multiracial background, and 1921 (0.3%) identified as Indigenous. The multivariate analysis demonstrated that race was significative to predict the death being that Black (OR = 1.43; 95% CI = 1.39-1.48), individuals with multiracial background (OR = 1.36; 95% CI = 1.34-1.38), and Indigenous (OR = 1.91; 95% CI = 1.70-2.15) races were more prone to die compared to the White race. The Asian individuals did not have a higher chance of dying due to SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to White individuals (OR = 0.99; 95% CI = 0.94-1.06). In addition, other characteristics contributed as such as being male (OR = 1.17; 95% CI = 1.16-1.19), age (mainly, +85 years old - OR = 23.02; 95% CI = 20.05-26.42) compared to 1-year-old individuals, living in rural areas (OR = 1.22; 95% CI = 1.18-1.26) or in peri-urban places (OR = 1.25; 95% CI = 1.11-1.40), and the presence of nosocomial infection (OR = 1.91; 95% CI = 1.82-2.01). Among the clinical symptoms, the main predictors were dyspnoea (OR = 1.25; 95% CI = 1.23-1.28), respiratory discomfort (OR = 1.30; 95% CI = 1.28-1.32), oxygen saturation <95% (OR = 1.40; 95% CI = 1.38-1.43). Also, among the comorbidities, the main predictors were the presence of immunosuppressive disorder (OR = 1.44; 95% CI = 1.39-1.49), neurological disorder (OR = 1.21; 95% CI = 1.17-1.25), hepatic disorder (OR = 1.41; 95% CI = 1.34-1.50), diabetes mellitus (OR = 1.40; 95% CI = 1.37-1.42), cardiopathy (OR = 1.13; 95%CI = 1.11-1.14), hematologic disorder (OR = 1.34; 95% CI = 1.24-1.43), Down syndrome (OR = 1.61; 95% CI = 1.43-1.81), renal disease (OR = 1.15; 95% CI = 1.11-1.18), and obesity (OR = 1.18; 95% CI = 1.15-1.21). Individuals on intensive care unit (OR = 2.25; 95% CI = 2.22-2.29) and on invasive (OR = 10.92; 95% CI = 10.66-11.18) or non-invasive (OR = 1.33; 95% CI = 1.30-1.35) mechanical ventilation were more prone to die.
Conclusions: Alongside several clinical symptoms and comorbidities, we associated race with an enhanced risk of death in Black individuals, individuals with multiracial backgrounds, and Indigenous peoples.
Copyright © 2022 by the Journal of Global Health. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of interest: The authors completed the ICMJE Disclosure of Interest Form (available upon request from the corresponding author), and declare no relevant interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome by SARS-CoV-2 Infection or Other Etiologic Agents Among Brazilian Indigenous Population: An Observational Study from the First Year of Coronavirus Disease (COVID)-19 Pandemic.Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022 Apr;8:100177. doi: 10.1016/j.lana.2021.100177. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2022. PMID: 35018359 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Clinical Features of Hospitalized Patients Due to the SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Absence of Comorbidities Regarding the Sex: An Epidemiological Study of the First Year of the Pandemic in Brazil.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 22;19(15):8895. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19158895. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35897265 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of influenza vaccination against coronavirus disease (COVID)-19 outcomes in hospitalized individuals in Brazil: an epidemiological study.Public Health. 2023 Dec;225:8-11. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2023.09.015. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37913610
-
The Digital Divide in Brazil and Barriers to Telehealth and Equal Digital Health Care: Analysis of Internet Access Using Publicly Available Data.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Jul 21;25:e42483. doi: 10.2196/42483. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 37477958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indigenous Races of the Earth, or New Chapters of Ethnological Inquiry.N Am Medchir Rev. 1857 Sep;1(5):665-688. N Am Medchir Rev. 1857. PMID: 38079702 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Ivermectin, Chloroquine/Hydroxychloroquine, and Azithromycin in Managing COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Phase III Clinical Trials.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 27;12(10):2206. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102206. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral co-detection of influenza virus and other respiratory viruses in hospitalized Brazilian patients during the first three years of the coronavirus disease (COVID)-19 pandemic: an epidemiological profile.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 16;15:1462802. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1462802. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39479210 Free PMC article.
-
Human genetic determinants of COVID-19 in Brazil: challenges and future plans.Genet Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 15;46(3 Suppl 1):e20230128. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2023-0128. eCollection 2024. Genet Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38226654 Free PMC article.
-
Profile of coronavirus disease enlightened asthma as a protective factor against death: An epidemiology study from Brazil during the pandemic.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 29;9:953084. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.953084. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36523782 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological Profile of Hospitalized Patients with Cystic Fibrosis in Brazil Due to Severe Acute Respiratory Infection during the COVID-19 Pandemic and a Systematic Review of Worldwide COVID-19 in Those with Cystic Fibrosis.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jul 4;11(13):1936. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11131936. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ko JY, Danielson ML, Town M, Derado G, Greenlund KJ, Kirley PD, et al. Risk Factors for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-Associated Hospitalization: COVID-19-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network and Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;72:e695-703. 10.1093/cid/ciaa1419 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
