Emerging therapeutic potential of adeno-associated virus-mediated gene therapy in liver fibrosis
- PMID: 35859692
- PMCID: PMC9271983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2022.06.009
Emerging therapeutic potential of adeno-associated virus-mediated gene therapy in liver fibrosis
Abstract
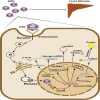
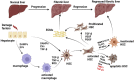
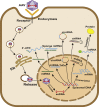
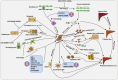
Liver fibrosis is a wound-healing response that results from various chronic damages. If the causes of damage are not removed or effective treatments are not given in a timely manner, it will progress to cirrhosis, even liver cancer. Currently, there are no specific medical therapies for liver fibrosis. Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated gene therapy, one of the frontiers of modern medicine, has gained more attention in many fields due to its high safety profile, low immunogenicity, long-term efficacy in mediating gene expression, and increasingly known tropism. Notably, increasing evidence suggests a promising therapeutic potential for AAV-mediated gene therapy in different liver fibrosis models, which helps to correct abnormally changed target genes in the process of fibrosis and improve liver fibrosis at the molecular level. Moreover, the addition of cell-specific promoters to the genome of recombinant AAV helps to limit gene expression in specific cells, thereby producing better therapeutic efficacy in liver fibrosis. However, animal models are considered to be powerless predictive of tissue tropism, immunogenicity, and genotoxic risks in humans. Thus, AAV-mediated gene therapy will face many challenges. This review systemically summarizes the recent advances of AAV-mediated gene therapy in liver fibrosis, especially focusing on cellular and molecular mechanisms of transferred genes, and presents prospective challenges.
Keywords: AAV; HSCs; cellular mechanism; gene therapy; liver fibrosis.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Adeno-associated Virus - A Safe and Promising Vehicle for Liverspecific Gene Therapy of Inherited and Non-inherited Disorders.Curr Gene Ther. 2017;17(1):4-16. doi: 10.2174/1566523217666170314141931. Curr Gene Ther. 2017. PMID: 28292253
-
Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated gene therapy for the treatment of ovarian cancer: a literature review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Sep;10(18):1024. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-4426. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36267784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The state of the art of adeno-associated virus-based vectors in gene therapy.Virol J. 2007 Oct 16;4:99. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-4-99. Virol J. 2007. PMID: 17939872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AAV-mediated liver-directed gene therapy.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;807:141-57. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-370-7_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 22034029 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and biological efficacy of an adeno-associated virus vector-cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator (AAV-CFTR) in the cystic fibrosis maxillary sinus.Laryngoscope. 1999 Feb;109(2 Pt 1):266-74. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199902000-00017. Laryngoscope. 1999. PMID: 10890777 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
CD73, a significant protein in liver diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 12;10:1147782. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1147782. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37122331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting thrombospondin-2 retards liver fibrosis by inhibiting TLR4-FAK/TGF-β signaling.JHEP Rep. 2024 Jan 24;6(3):101014. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2024.101014. eCollection 2024 Mar. JHEP Rep. 2024. PMID: 38379585 Free PMC article.
-
Liver directed adeno-associated viral vectors to treat metabolic disease.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2024 Jan;47(1):22-40. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12637. Epub 2023 Jun 5. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2024. PMID: 37254440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Models and Promising Pharmacotherapeutic Strategies in Liver Fibrosis: An Update.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 May 11;45(5):4246-4260. doi: 10.3390/cimb45050270. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37232739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular mechanotransduction in health and diseases: from molecular mechanism to therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jul 31;8(1):282. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01501-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37518181 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marcellin P., Kutala B.K. Liver diseases: a major, neglected global public health problem requiring urgent actions and large-scale screening. Liver Int. 2018;38:2–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

