Real-world outcomes, treatment patterns and T790M testing rates in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line first- or second-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors from the Slovenian cohort of the REFLECT study
- PMID: 35853681
- PMCID: PMC9400443
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2022-0025
Real-world outcomes, treatment patterns and T790M testing rates in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line first- or second-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors from the Slovenian cohort of the REFLECT study
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are effective treatments for EGFR mutation-positive (EGFRm) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, routine clinical practice is different between countries/institutions.
Patients and methods: The REFLECT study (NCT04031898) is a retrospective medical chart review that explored real-life treatment and outcomes of EGFRm NSCLC patients receiving first-line (1L) first-/second-generation (1G/2G) EGFR TKIs in 8 countries. This study included adult patients with documented advanced/metastatic EGFRm NSCLC with 1L 1G/2G EGFR TKIs initiated between Jan 2015 - Jun 2018. We reviewed data on clinical characteristics, treatments, EGFR/T790M testing patterns, and survival outcomes. Here, we report data from 120 medical charts in 3 study sites from Slovenia.
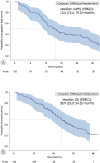
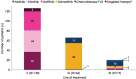
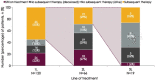
Results: The Slovenian cohort (median age 70 years, 74% females) received 37% erlotinib, 32% afatinib, 31% gefitinib. At the time of data collection, 94 (78%) discontinuations of 1L TKI, and 89 (74%) progression events on 1L treatment were reported. Among patients progressing on 1L, 73 (82%) were tested for T790M mutation yielding 50 (68%) positive results, and 62 (85%) received 2L treatment. 82% of patients received osimertinib. Attrition rate between 1L and 2L was 10%. The median (95% CI) real-world progression free survival on 1L EGFR TKIs was 15.6 (12.6, 19.2) months; median overall survival (95% CI) was 28.9 (25.0, 34.3) months.
Conclusions: This real-world study provides valuable information about 1G/2G EGFR TKIs treatment outcomes and attrition rates in Slovenian EGFRm NSCLC patients. The reduced attrition rate and improved survival outcomes emphasize the importance of 1L treatment decision.
Keywords: T790M testing; attrition; epidermal growth factor receptor; non-small cell lung cancer; real-world study.
© 2022 Nina Turnsek, Rok Devjak, Natalija Edelbaher, Ilonka Osrajnik, Mojca Unk, Dusanka Vidovic, Tina Jeric, Urska Janzic, published by Sciendo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-World Testing Practices, Treatment Patterns and Clinical Outcomes in Patients from Central Eastern Europe with EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Chart Review Study (REFLECT).Curr Oncol. 2022 Aug 17;29(8):5833-5845. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29080460. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36005198 Free PMC article.
-
Observational Study of Treatment Patterns in Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer After First-Line EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Adv Ther. 2020 Feb;37(2):946-954. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01221-4. Epub 2020 Jan 18. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 31955357
-
Real-world treatment patterns of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Cancer Med. 2023 Jan;12(1):159-169. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4918. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 35702932 Free PMC article.
-
Afatinib as First-Line Treatment in Asian Patients with EGFR Mutation-Positive NSCLC: A Narrative Review of Real-World Evidence.Adv Ther. 2021 May;38(5):2038-2053. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01696-9. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 33730350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the prognostic value of the new 9th edition Tumor-Node-Metastases (TNM) staging system for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung adenocarcinoma patients with bone metastases.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Oct 11;24(1):508. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03331-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39394157 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer care treatment attrition in adults: Measurement approaches and inequities in patient dropout rates - a rapid review.BMC Cancer. 2024 Nov 1;24(1):1345. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13096-7. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39482591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K, Novello S, Smit EF, Faivre-Finn C. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis. treatment and follow-up [published correction appears in Ann Oncol. 2019;30:863–70. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy275. et al. Ann Oncol 2018; 29(Suppl 4): iv192-237. - DOI - PubMed
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). GLOBOCAN 2020. Cancer today. Lung. [internet]. [cited 2021 Feb 16] https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/15-Lung-fact-sheet.pdf World Health Organization. Available at.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
