Could Repeated Cardio-Renal Injury Trigger Late Cardiovascular Sequelae in Extreme Endurance Athletes?
- PMID: 35851948
- PMCID: PMC9691495
- DOI: 10.1007/s40279-022-01734-8
Could Repeated Cardio-Renal Injury Trigger Late Cardiovascular Sequelae in Extreme Endurance Athletes?
Abstract
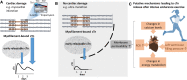
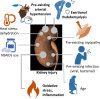
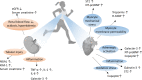
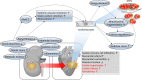
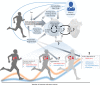
Regular exercise confers multifaceted and well-established health benefits. Yet, transient and asymptomatic increases in markers of cardio-renal injury are commonly observed in ultra-endurance athletes during and after competition. This has raised concerns that chronic recurring insults could cause long-term cardiac and/or renal damage. Indeed, extreme endurance exercise (EEE) over decades has sometimes been linked with untoward cardiac effects, but a causal relation with acute injury markers has not yet been established. Here, we summarize the current knowledge on markers of cardiac and/or renal injury in EEE athletes, outline the possible interplay between cardiac and kidney damage, and explore the roles of various factors in the development of potential exercise-related cardiac damage, including underlying diseases, medication, sex, training, competition, regeneration, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation. In conclusion, despite the undisputed health benefits of regular exercise, we speculate, based on the intimate link between heart and kidney diseases, that in rare cases excessive endurance sport may induce adverse cardio-renal interactions that under specific, hitherto undefined conditions could result in persistent cardiac damage. We highlight future research priorities and provide decision support for athletes and clinical consultants who are seeking safe strategies for participation in EEE training and competition.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
James Keefe is a participant in the Speaker Bureau for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Janssen and Lilly. He is also Chief Medical Officer and Founder of CardioTabs, a nutraceutical company, and has a major ownership interest in that company. Hans-Georg Predel holds a leadership position in the German Hypertension Society. Johannes Burtscher, Paul-Emmanuel Vanderriele, Matthieu Legrand, Josef Niebauer, Grégoire Millet and Martin Burtscher declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomarkers of Cardiac Stress and Injury in Athletes: What Do They Mean?Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2018 Apr;15(2):116-122. doi: 10.1007/s11897-018-0385-9. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2018. PMID: 29520707 Review.
-
Metabolic markers in sports medicine.Adv Clin Chem. 2012;56:1-54. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-394317-0.00015-7. Adv Clin Chem. 2012. PMID: 22397027 Review.
-
Master Endurance Athletes and Cardiovascular Controversies.Curr Sports Med Rep. 2020 Mar;19(3):113-118. doi: 10.1249/JSR.0000000000000695. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32141906 Review.
-
[ATHLETE'S HEART - THE MORE THE MERRIER?].Harefuah. 2016 Sep;155(9):531-536. Harefuah. 2016. PMID: 28530078 Review. Hebrew.
-
Potential Long-Term Health Problems Associated with Ultra-Endurance Running: A Narrative Review.Sports Med. 2022 Apr;52(4):725-740. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01561-3. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 34542868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Atrial Fibrillation in Endurance Training Athletes: Scoping Review.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 May 26;24(6):155. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2406155. eCollection 2023 Jun. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39077536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How much resistance exercise is beneficial for healthy aging and longevity?J Sport Health Sci. 2023 May;12(3):284-286. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2022.11.004. Epub 2022 Nov 7. J Sport Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 36356853 Free PMC article.
-
Regular exercise delays microvascular endothelial dysfunction by regulating antioxidant capacity and cellular metabolism.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 17;13(1):17671. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44928-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37848614 Free PMC article.
-
Acute effects of exercise-induced muscle damage on sprint and change of direction performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Biol Sport. 2024 Jul;41(3):153-168. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2024.131823. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Biol Sport. 2024. PMID: 38952917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new perspective on cardiovascular function and dysfunction during endurance exercise: identifying the primary cause of cardiovascular risk.Biol Sport. 2024 Oct;41(4):131-144. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2024.134757. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Biol Sport. 2024. PMID: 39416509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wen CP, Wai JPM, Tsai MK, Yang YC, Cheng TYD, Lee M-C, et al. Minimum amount of physical activity for reduced mortality and extended life expectancy: a prospective cohort study. The lancet. 2011;378(9798):1244–1253. - PubMed
-
- Whyte G, Sheppard M, George K, Shave R, Wilson M, Prasad S, et al. Post-mortem evidence of idiopathic left ventricular hypertrophy and idiopathic interstitial myocardial fibrosis: is exercise the cause? Br J Sports Med. 2008;42(4):304–305. - PubMed

