Sanguinarine Regulates Tumor-Associated Macrophages to Prevent Lung Cancer Angiogenesis Through the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway
- PMID: 35847885
- PMCID: PMC9282876
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.732860
Sanguinarine Regulates Tumor-Associated Macrophages to Prevent Lung Cancer Angiogenesis Through the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway
Abstract
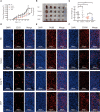
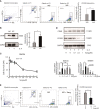
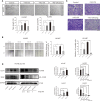
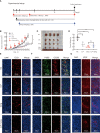
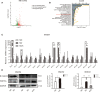
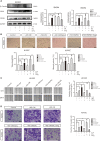
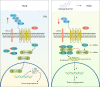
Tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-mediated angiogenesis in the tumor microenvironment is a prerequisite for lung cancer growth and metastasis. Therefore, targeting TAMs, which block angiogenesis, is expected to be a breakthrough in controlling the growth and metastasis of lung cancer. In this study, we found that Sanguinarine (Sang) inhibits tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis of subcutaneously transplanted tumors in Lewis lung cancer mice. Furthermore, Sanguinarine inhibited the proliferation, migration, and lumen formation of HUVECs and the expression of CD31 and VEGF by regulating the polarization of M2 macrophages in vitro. However, the inhibitory effect of Sanguinarine on angiogenesis remained in vivo despite the clearance of macrophages using small molecule drugs. Further high-throughput sequencing suggested that WNT/β-Catenin signaling might represent the underlying mechanism of the beneficial effects of Sanguinarine. Finally, the β-Catenin activator SKL2001 antagonized the effect of Sanguinarine, indicating that Sanguinarine can regulate M2-mediated angiogenesis through the WNT/β-Catenin pathway. In conclusion, this study presents the first findings that Sanguinarine can function as a novel regulator of the WNT/β-Catenin pathway to modulate the M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit angiogenesis, which has potential application value in immunotherapy and antiangiogenic therapy for lung cancer.
Keywords: Wnt/β- catenin; angiogenesis; lung cancer; sanguinarine; tumor associated macrophages.
Copyright © 2022 Cui, Luo, Qian, Tian, Fang, Wang, Zeng, Wu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crosstalk between hepatic tumor cells and macrophages via Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes M2-like macrophage polarization and reinforces tumor malignant behaviors.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jul 18;9(8):793. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0818-0. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30022048 Free PMC article.
-
Zoledronic acid inhibits thyroid cancer stemness and metastasis by repressing M2-like tumor-associated macrophages induced Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 1;256:117925. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117925. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32522570
-
MORC2 Enhances Tumor Growth by Promoting Angiogenesis and Tumor-Associated Macrophage Recruitment via Wnt/β-Catenin in Lung Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(4):1679-1694. doi: 10.1159/000495673. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30504718
-
Angiogenesis-Related Functions of Wnt Signaling in Colorectal Carcinogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 2;12(12):3601. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123601. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33276489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis initiation under normoxic conditions through Wnt/β-catenin pathway in gliomas.Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jan 26;29(1):71-91. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2017-0032. Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 28822229 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural compounds: Wnt pathway inhibitors with therapeutic potential in lung cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 28;14:1250893. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1250893. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37841927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sanguinarine promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating the miR-497-5p/CDK4 axis.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Dec 15;14(12):8539-8551. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36628219 Free PMC article.
-
Research advances on signaling pathways regulating the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 31;15:1452078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1452078. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39144141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage-Myofibroblast Transition Contributes to Myofibroblast Formation in Proliferative Vitreoretinal Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 31;24(17):13510. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713510. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686317 Free PMC article.
-
A review of natural products targeting tumor immune microenvironments for the treatment of lung cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 1;15:1343316. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343316. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38361933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

