Ablation of PI3K-p110alpha Impairs Maternal Metabolic Adaptations to Pregnancy
- PMID: 35846351
- PMCID: PMC9283861
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.928210
Ablation of PI3K-p110alpha Impairs Maternal Metabolic Adaptations to Pregnancy
Abstract
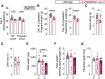
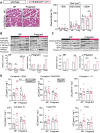
Pregnancy requires adaptations in maternal metabolism to support fetal growth. The phosphoinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signalling pathway controls multiple biological processes and defects in this pathway are linked to metabolic disorders including insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in non-pregnant animals. However, relatively little is known about the contribution of PI3K signalling to the maternal metabolic adaptations during pregnancy. Using mice with partial inactivation of the PI3K isoform, p110α (due to a heterozygous dominant negative mutation; Pik3ca-D933A), the effects of impaired PI3K-p110α signalling on glucose and insulin handling were examined in the pregnant and non-pregnant states and related to the morphological, molecular, and mitochondrial changes in key metabolic organs. The results show that non-pregnant mice lacking PI3K-p110α are glucose intolerant but exhibit compensatory increases in pancreatic glucose-stimulated insulin release and adipose tissue mitochondrial respiratory capacity and fatty acid oxidation. However, in pregnancy, mutant mice failed to show the normal increment in glucose intolerance and pancreatic β-cell mass observed in wild-type pregnant dams and exhibited further enhanced adipose tissue mitochondrial respiratory capacity. These maladaptations in pregnant mutant mice were associated with fetal growth restriction. Hence, PI3K-p110α is a key regulator of metabolic adaptations that support fetal growth during normal pregnancy.
Keywords: PI3K; metabolism; mitochondria; pregnancy; signalling.
Copyright © 2022 Lopez-Tello, Salazar-Petres, Webb, Fowden and Sferruzzi-Perri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Maternal and Fetal PI3K-p110α Deficiency Induces Sex-Specific Changes in Conceptus Growth and Placental Mitochondrial Bioenergetic Reserve in Mice.Vet Sci. 2022 Sep 13;9(9):501. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9090501. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36136716 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced β-adrenergic signalling underlies an age-dependent beneficial metabolic effect of PI3K p110α inactivation in adipose tissue.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 4;10(1):1546. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09514-1. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30948720 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role for the p110alpha phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase in growth and metabolic regulation.Nature. 2006 May 18;441(7091):366-70. doi: 10.1038/nature04694. Epub 2006 Apr 12. Nature. 2006. PMID: 16625210
-
Pregnancy-induced changes in β-cell function: what are the key players?J Physiol. 2022 Mar;600(5):1089-1117. doi: 10.1113/JP281082. Epub 2021 Apr 4. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 33704799 Review.
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal and Intrauterine Influences on Feto-Placental Growth Are Accompanied by Sexually Dimorphic Changes in Placental Mitochondrial Respiration, and Metabolic Signalling Pathways.Cells. 2023 Mar 3;12(5):797. doi: 10.3390/cells12050797. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899933 Free PMC article.
-
Placental adaptations supporting fetal growth during normal and adverse gestational environments.Exp Physiol. 2023 Mar;108(3):371-397. doi: 10.1113/EP090442. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Exp Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36484327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal and Fetal PI3K-p110α Deficiency Induces Sex-Specific Changes in Conceptus Growth and Placental Mitochondrial Bioenergetic Reserve in Mice.Vet Sci. 2022 Sep 13;9(9):501. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9090501. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36136716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aoyagi K., Ohara-Imaizumi M., Nishiwaki C., Nakamichi Y., Ueki K., Kadowaki T., et al. (2012). Acute Inhibition of PI3K-PDK1-Akt Pathway Potentiates Insulin Secretion through Upregulation of Newcomer Granule Fusions in Pancreatic β-Cells. PLoS ONE 7, e47381. 10.1371/journal.pone.0047381 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

