The Correlation between the Level of Skin Advanced Glycation End Products in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy and the Types of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome
- PMID: 35845597
- PMCID: PMC9286975
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5193944
The Correlation between the Level of Skin Advanced Glycation End Products in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy and the Types of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to analyze the correlation between the level of skin advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients and the diabetic retinopathy (DR) staging in different traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndromes.
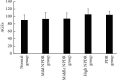
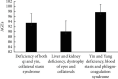
Methods: 416 T2DM patients were divided into normal group, nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) group (mild, moderate, and severe), and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) group according to the DR grade. Patients' height, weight, fasting blood glucose (FBG), hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c), blood lipid, renal function, and skin AGEs were measured. According to TCM syndrome differentiation criteria, 230 patients with T2DM and DR were divided into I. qi and yin deficiency, collateral stasis group; II. liver and kidney deficiency, eye collaterals loss group; and III. yin and yang deficiency, blood stasis, and phlegm coagulation group.
Results: The skin AGEs levels of different DR staging groups were statistically significant (P < 0.05), and the skin AGEs levels in the mild and moderate NPDR groups were significantly higher (P < 0.05) than those of the normal group. It was significantly higher (P < 0.05) in the severe NPDR group than in the normal group, mild and moderate NPDR groups. The skin AGEs levels of the PDR group were significantly higher (P < 0.05) than the normal group, mild and moderate NPDR groups. It was positively correlated with DR stage, HbA1c, total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and urine metal analysis (UMA) (r = 0.467, 0.411, 0.413, 0.503, 0.424, P < 0.05). The skin AGEs levels of the qi and yin deficiency and collaterals stasis syndrome group were significantly higher (P < 0.05) than in the liver and kidney deficiency and eye collaterals loss groups. It was also significantly higher (P < 0.05) in yin and yang deficiency, blood stasis, and phlegm coagulation syndrome groups than in qi and yin deficiency and collaterals stasis syndrome groups.
Conclusion: There is a positive correlation between skin AGEs and DR staging in T2DM patients. Skin AGEs level is predictive for the risk of DR complications in T2DM patients and is vital in assessing DR degree per TCM syndrome type.
Copyright © 2022 Senwei Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors reported that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Association of choroidal thickness with diabetic retinopathy at different stages].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Aug 25;95(32):2584-8. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26711604 Chinese.
-
[Characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine syndromes in patients with acute ischemic stroke of yin or yang syndrome: a multicenter trial].Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008 Apr;6(4):346-51. doi: 10.3736/jcim20080404. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18405599 Chinese.
-
Distribution of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes in diabetic kidney disease chronic kidney disease 1-5: a correlation study.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Jun;44(3):572-580. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230802.007. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38767642 Free PMC article.
-
[Syndrome Types of Chinese Medicine and Clinical Characteristics of 660 Patients with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2017 Jan;37(1):62-67. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 30695427 Chinese.
-
[Study on the correlation between Chinese medicine syndrome types of the Uighur and Han people and levels of blood lipids and fibrinogen in premature coronary heart disease patients].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;32(4):478-81. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22803427 Chinese.
Cited by
-
HHO optimized support vector machine classifier for traditional Chinese medicine syndrome differentiation of diabetic retinopathy.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun 18;17(6):991-1000. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.06.02. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38895691 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Glycation End-Products and Diabetic Neuropathy of the Retina.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2927. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032927. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous advanced glycation end products in the pathogenesis of chronic diabetic complications.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Sep 15;9:1002710. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1002710. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36188225 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lai M. C., Liu W. Y., Liou S. S., Liu I. M. The citrus flavonoid hesperetin encounters diabetes-mediated alzheimer-type neuropathologic changes through relieving advanced glycation end-products inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nutrients . 2022;14:p. 745. doi: 10.3390/nu14040745. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources