A study of apolipoprotein A1(ApoA1) and interleukin-10(IL-10) in diabetes with foot ulcers
- PMID: 35836916
- PMCID: PMC9236711
- DOI: 10.37796/2211-8039.1279
A study of apolipoprotein A1(ApoA1) and interleukin-10(IL-10) in diabetes with foot ulcers
Abstract
Background: The high morbidity, mortality and associated economic burden have entailed to identifying early biomarker of diabetic foot ulcers (DFU). Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory molecules play a role in the chronic inflammation associated with diabetic foot ulcers (DFU).
Aim: This study aims to find the association between ApoA1, IL-10, TNF-α and diabetic foot ulcers, and whether their levels can assess the severity of the disease.
Method: Two groups, diabetic mellitus without foot ulcers and diabetes with foot ulcers were recruited for the study. Detailed clinical history was obtained and blood was collected to measure TNF-α , IL-10 and Apo A1. The association between variables was analysed using Pearson correlation test. ROC analysis was used to identify cut-off values of ApoA1, IL-10 and TNF-α in diabetes patients with foot ulcers.
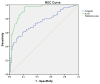
Results: The presence of pro-inflammatory parameter, TNF-α , was higher and anti-inflammatory biomarkers, HDL, ApoA1 and IL-10 were lower in patients of DFU than those without foot ulcers (p < 0.001). Increasing age, smoking, retinopathy, eGFR and inflammatory biomarkers like low levels of ApoA1 (p < 0.005) and IL-10 (p < 0.001) significantly contributed to the development of diabetic foot ulcers. ROC curve identified the cut-off for ApoA1 and IL-10 as 89.82mg/dL and 78.80pg/mL respectively.
Conclusion: In the light of this study, ApoA1 has the potential to predict DFU. The finding proposes IL-10 (b = -0.37, p < 0.001) could be considered in stratifying DFU as per its severity.
Keywords: ApoA1; Cytokines; Diabetic foot ulcers; TNF-α; Wagners; eGFR.
© the Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest No conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Raised serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in patients with active diabetic foot ulcers.Br J Nutr. 2016 Jun;115(11):1938-46. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516001094. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27153203
-
Correlation of Long Non-coding RNA LncRNA-FA2H-2 With Inflammatory Markers in the Peripheral Blood of Patients With Coronary Heart Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Jun 21;8:682959. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.682959. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34235188 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning algorithm to evaluate risk factors of diabetic foot ulcers and its severity.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022 Aug;60(8):2349-2357. doi: 10.1007/s11517-022-02617-w. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022. PMID: 35751828
-
The role of CXCL8 in chronic nonhealing diabetic foot ulcers and phenotypic changes in fibroblasts: a molecular perspective.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):1565-1572. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07144-3. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35044539 Review.
-
Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Vitamin D Status: A Literature Review.SAGE Open Nurs. 2018 Sep 7;4:2377960818789027. doi: 10.1177/2377960818789027. eCollection 2018 Jan-Dec. SAGE Open Nurs. 2018. PMID: 33415199 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomics-driven drug repositioning for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 20;13(1):10032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37120-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37340026 Free PMC article.
-
Combined with dynamic serum proteomics and clinical follow-up to screen the serum proteins to promote the healing of diabetic foot ulcer.Endocrine. 2024 May;84(2):365-379. doi: 10.1007/s12020-023-03579-1. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 37938414
-
Exosomes isolated from IMMUNEPOTENT CRP, a hemoderivative, to accelerate diabetic wound healing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 May 20;12:1356028. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1356028. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38835975 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Polyinosinic-Polycytidylic Acid-Induced Acute Pulmonary Inflammation and NF-κB Activation in Mice by a Banana Plant Extract.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Jan 1;21(1):107-122. doi: 10.7150/ijms.88748. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38164360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel S, Maheswari A, Chandra A. Biomarkers for wound healing and their evaluation. J Wound Care. 2016;25(1):46–55. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous