VEGF/VEGFR-Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 35813484
- PMCID: PMC9254480
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.70958
VEGF/VEGFR-Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
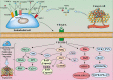
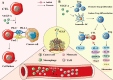
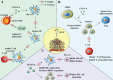
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the leading cause of death by cancer worldwide. Despite developments in therapeutic approaches for the past few decades, the 5-year survival rate of patients with NSCLC remains low. NSCLC tumor is a complex, heterogeneous microenvironment, comprising blood vessels, cancer cells, immune cells, and stroma cells. Vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) are a major mediator to induce tumor microvasculature and are associated with the progression, recurrence, and metastasis of NSCLC. Current treatment medicines targeting VEGF/VEGF receptor (VEGFR) pathway, including neutralizing antibodies to VEGF or VEGFR and receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors, have shown good treatment efficacy in patients with NSCLC. VEGF is not only an important angiogenic factor but also an immunomodulator of tumor microenvironment (TME). VEGFs can suppress antigen presentation, stimulate activity of regulatory T (Treg) cells, and tumor-associated macrophages, which in turn promote an immune suppressive microenvironment in NSCLC. The present review focuses on the angiogenic and non-angiogenic functions of VEGF in NSCLC, especially the interaction between VEGF and the cellular components of the TME. Additionally, we discuss recent preclinical and clinical studies to explore VEGF/VEGFR-targeted compounds and immunotherapy as novel approaches targeting the TME for the treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: NSCLC; VEGF/VEGFR pathway; clinical trials; immunotherapy; tumor microenvironment.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blocking CD47 efficiently potentiated therapeutic effects of anti-angiogenic therapy in non-small cell lung cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Dec 11;7(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0812-9. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31829270 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting angiogenesis in squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Drugs. 2014 Mar;74(4):403-13. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0182-z. Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24578213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic implication of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) targeting in cancer cells and tumor microenvironment by competitive and non-competitive inhibitors.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Oct;136:97-107. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.023. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30170190 Review.
-
The HGF/c-MET Pathway Is a Driver and Biomarker of VEGFR-inhibitor Resistance and Vascular Remodeling in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 15;23(18):5489-5501. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-3216. Epub 2017 May 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28559461 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine signaling by VEGF-C promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell metastasis via recruitment of tumor-associated macrophages.Exp Cell Res. 2018 Mar 15;364(2):208-216. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.02.005. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Exp Cell Res. 2018. Retraction in: Exp Cell Res. 2020 Sep 1;394(1):112195. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112195 PMID: 29427623 Retracted.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of CLEC11A and its derived immune signature in gastric cancer.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 29;15:1324959. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1324959. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38348052 Free PMC article.
-
Advancement of regulating cellular signaling pathways in NSCLC target therapy via nanodrug.Front Chem. 2023 Sep 7;11:1251986. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1251986. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37744063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles overcome adaptive immune resistance and enhance immunotherapy via targeting tumor microenvironment in lung cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 24;14:1130937. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1130937. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37033636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced recovery of postoperative nursing for single-port thoracoscopic surgery in lung cancer patients.Front Oncol. 2023 May 23;13:1163338. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1163338. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37287915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound combined with microbubble mediated immunotherapy for tumor microenvironment.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 29;15:1304502. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1304502. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38487163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

