N6-Methyladenosine Modification Patterns and Tumor Microenvironment Immune Characteristics Associated With Clinical Prognosis Analysis in Stomach Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35813200
- PMCID: PMC9261346
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.913307
N6-Methyladenosine Modification Patterns and Tumor Microenvironment Immune Characteristics Associated With Clinical Prognosis Analysis in Stomach Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
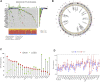
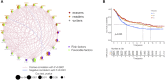
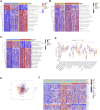
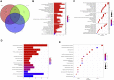
Background: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is a part of epigenetic research that has gained increasing attention in recent years. m6A modification is widely involved in many biological behaviors of intracellular RNA by regulating mRNA, thus affecting disease progression and tumor occurrence. However, the effects of m6A modification on immune cell infiltration of the tumor microenvironment (TME) are uncertain in stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD). Methods: The Cancer Genome Map (TCGA) database was used to download transcriptome data, clinicopathological data, and survival data for m6A-regulated genes in 433 STAD tissues that meet the requirements of this study. GSE84437 data were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The correlation between 23 m6A regulated genes was analyzed using R software. Sample clustering analysis was carried out on the genes of the m6A regulatory factor, and survival analysis and differentiation comparison were made for patients in clustering grouping. Then, the Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA), the single-sample GSEA (ssGSEA), and other methods were conducted to assess the correlation among m6A modification patterns, TME cell infiltration characteristics, and immune infiltration markers. The m6A modification pattern of individual tumors was quantitatively evaluated using the m6A score scheme of the principal component analysis (PCA). Results: From the TCGA database, 94/433 (21.71%) samples were somatic cell mutations, and ZC3H13 mutations are the most common. Based on the consensus, matrix k-3 is an optimal clustering stability value to identify three different clusters. Three types of m6A methylation modification patterns were significantly different in immune infiltration. Thus, 1028 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified. The survival analysis of the m6A score found that patients in the high m6A score group had a better prognosis than those in the low m6A score group. Further analysis of the survival curve combining tumor mutation burden (TMB) and m6A scores revealed that patients had a significantly lower prognosis in the low tumor mutant group and the low m6A score group (p = 0.003). The results showed that PD-L1 was significantly higher in the high m6A score group than in the low score group (p < 2.22e-16). The high-frequency microsatellite instability (MSI-H) subtype score was significantly different from the other two groups. Conclusions: This study systematically evaluated the modification patterns of 23 m6A regulatory factors in STAD. The m6A modification pattern may be a critical factor leading to inhibitory changes and heterogeneity in TME. This elucidated the TME infiltration characteristics in patients with STAD through the evaluation of the m6A modification pattern.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; immunotherapy; microsatellites instability; mutation burden; stomach adenocarcinoma; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Meijing, Tianhang and Biao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
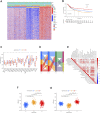
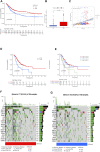
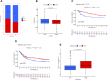
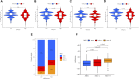
Similar articles
-
Constructing and validating of m6a-related genes prognostic signature for stomach adenocarcinoma and immune infiltration: Potential biomarkers for predicting the overall survival.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 22;12:1050288. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1050288. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36620557 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analyses of m6A Regulator-Based Signature on Its Clinical Application and Immunogenomic Landscape in Stomach Adenocarcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 20;2022:2053719. doi: 10.1155/2022/2053719. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36193316 Free PMC article.
-
A signature based on m6A pattern and tumor microenvironment infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jul 15;14(7):4931-4947. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35958449 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of nucleotide metabolism and neuroendocrine regulation-associated modification patterns in stomach adenocarcinoma with auxiliary prognostic assessment and immunotherapy response prediction.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 16;13:1076521. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1076521. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36726460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification and noncoding RNA in tumor microenvironment.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Apr 17;19(7):2198-2219. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.79651. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37151887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Constructing and validating of m6a-related genes prognostic signature for stomach adenocarcinoma and immune infiltration: Potential biomarkers for predicting the overall survival.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 22;12:1050288. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1050288. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36620557 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an immunogenic cell death prognostic signature for predicting clinical outcome and immune infiltration characterization in stomach adenocarcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Oct 19;15(20):11389-11411. doi: 10.18632/aging.205132. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37862109 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 promotes drug resistance to oxaliplatin in gastric cancer cells through DNA repair pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 26;14:1257410. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1257410. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37822880 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine methylation regulates the tumor microenvironment of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Jun 15;16(6):2555-2570. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i6.2555. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38994134 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analyses of m6A Regulator-Based Signature on Its Clinical Application and Immunogenomic Landscape in Stomach Adenocarcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 20;2022:2053719. doi: 10.1155/2022/2053719. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36193316 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

