KIFC3 Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Colorectal Cancer via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 35812733
- PMCID: PMC9257096
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.848926
KIFC3 Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Colorectal Cancer via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
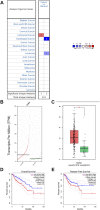
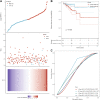
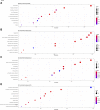
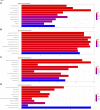
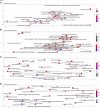
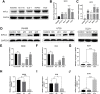
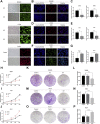
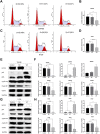
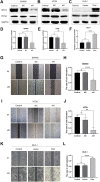
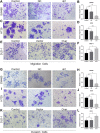
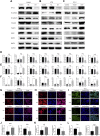
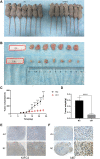
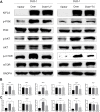
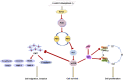
Background: KIFC3, belongs to kinesin superfamily proteins (KIFs), is well known for its role in intracellular cargo movement. KIFC3 has been identified as a docetaxel resistance gene in breast cancer cells, however, the role of KIFC3 and its potential mechanism in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains elusive. Objectives: We aims to investigate the effects of KIFC3 in proliferation, migration, and invasion in CRC as well as the potential mechanism inside. Methods: We investigated the expression of KIFC3 in the Oncomine, Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis databases. The KIFC3 protein expression and mRNA level in CRC cells were evaluated by western blot and qRT-PCR. Cell proliferation ability was detected by CCK-8, EdU, colony formation assay and xenograft tumor in nude mice. Flow cytometry was used to detect the cell cycle. The effect of KIFC3 on the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) was investigated by transwell and wound healing assay. The association of KIFC3 with EMT and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway were measured by western blot and immunofluorescence staining. Results: The expression of KIFC3 was higher in CRC tissues than normal colorectal tissue, and was negatively correlated with the overall survival of patients with CRC. KIFC3 silencing inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC cells. Meanwhile, it could decrease the number of cells in S phase. KIFC3 silencing inhibited the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen, Cyclin A2, Cyclin E1, and CDK2 and increased the expression of p21 and p53. KIFC3 overexpression promoted the G1/S phase transition. KIFC3 silencing inhibited the EMT process, which decreased the level of N-cadherin, Vimentin, SNAIL 1, TWIST, MMP-2, MMP-9 and increased E-cadherin, while KIFC3 overexpression show the opposite results. Furthermore, the knockdown of KIFC3 suppressed the EMT process by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. KIFC3 silencing decreased the expression of phosphorylated PI3K, AKT, mTOR, but total PI3K, AKT, mTOR have no change. Inversely, the upregulation of KIFC3 increased the expression of phosphorylated PI3K, AKT and mTOR, total PI3K, AKT, mTOR have no change. In a xenograft mouse model, the depletion of KIFC3 suppressed tumor growth. the increased expression levels of KIFC3 could enhance the proliferation, migration and invasion of CRC cells, and enhance the EMT process through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Conclusion: Our study substantiates that KIFC3 can participate in the regulation of CRC progression by which regulates EMT via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis.
Keywords: KIFC3; PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal pathway; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; invasion; migration; proliferation.
Copyright © 2022 Liao, Zhang, Lu, Li and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ARHGAP9 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation, invasion and EMT via targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Tissue Cell. 2022 Aug;77:101817. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2022.101817. Epub 2022 May 7. Tissue Cell. 2022. PMID: 35679685
-
Effects of miR-202-5p silencing PIK3CA gene expression on proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer SiHa cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway activation.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Nov;476(11):4031-4044. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04211-4. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34244973
-
KIFC3 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by activating EMT and β-catenin signaling.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Jul 15;14(7):1239-1251. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i7.1239. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36051093 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway and Its Role in Cancer Therapeutics: Are We Making Headway?Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 24;12:819128. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.819128. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35402264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/AKT pathway as a pivotal regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung tumor cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 May 10;24(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03357-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38730433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oncogenic zinc finger protein ZNF687 accelerates lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and tumor progression by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Thorac Cancer. 2023 May;14(14):1223-1238. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14856. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Thorac Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36944484 Free PMC article.
-
THBS1-Mediated Degradation of Collagen via the PI3K/AKT Pathway Facilitates the Metastasis and Poor Prognosis of OSCC.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 28;24(17):13312. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713312. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686118 Free PMC article.
-
3,3'-((3,4,5-trifluoropHenyl)methylene)bis(4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one) inhibit lung cancer cell proliferation and migration.PLoS One. 2024 May 22;19(5):e0303186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303186. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38776295 Free PMC article.
-
KIFC3 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 3;14(1):20471. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71602-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39227687 Free PMC article.
-
Arctigenin inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer through epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 27;19(9):e0308947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308947. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39331595 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

