Vitamin D Status, Cardiovascular Risk Profile, and miRNA-21 Levels in Hypertensive Patients: Results of the HYPODD Study
- PMID: 35807864
- PMCID: PMC9268320
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14132683
Vitamin D Status, Cardiovascular Risk Profile, and miRNA-21 Levels in Hypertensive Patients: Results of the HYPODD Study
Abstract
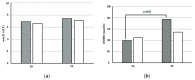
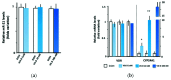
The vitamin D and microRNA (miR) systems may play a role in the pathogenesis of cardiometabolic disorders, including hypertension. The HYPODD study was a double-blind placebo-controlled trial aiming to assess the effects of cholecalciferol treatment in patients with well-controlled hypertension and hypovitaminosis D (25OHD levels < 50 nmol/L). In addition to this clinical trial, we also evaluated the effects of cholecalciferol and calcitriol treatment on miR-21 expression in vivo and in vitro, respectively. Changes in the cardiovascular risk profiles were evaluated in HYPODD patients treated with cholecalciferol (C-cohort) or with placebo (P-cohort). The miR-21circulating levels were measured in four C-cohort patients and five P-cohort patients. In vitro, the miR-21 levels were measured in HEK-293 cells treated with calcitriol or with ethanol vehicle control. Cholecalciferol treatment increased 25OHD levels and reduced parathormone, total cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in C-cohort patients, whereas no significant changes in these parameters were observed in P-cohort patients. The miR-21 circulating levels did not change in the C- or the P-cohort patients upon treatment. Calcitriol treatment did not affect miR-21 levels in HEK-293 cells. In conclusion, hypovitaminosis D correction ameliorated the cardiovascular risk profiles in hypertensive patients treated with cholecalciferol but did not influence the miR-21 expression.
Keywords: calcitriol; cholecalciferol; clinical trial; hypertension; hypovitaminosis D; inflammation; miR-21.
Conflict of interest statement
D.R. has previously consulted for Kyowa Kyrin. The other authors declare no conflict of interest. ABIOGEN had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypovitaminosis D and organ damage in patients with arterial hypertension: a multicenter double blind randomised controlled trial of cholecalciferol supplementation (HYPODD) : study design, clinical procedures and treatment protocol.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2015 Jun;22(2):135-42. doi: 10.1007/s40292-015-0080-9. Epub 2015 Mar 14. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2015. PMID: 25771895 Clinical Trial.
-
Vitamin D Status in Paget Disease of Bone and Efficacy-Safety Profile of Cholecalciferol Treatment in Pagetic Patients with Hypovitaminosis D.Calcif Tissue Int. 2019 Oct;105(4):412-422. doi: 10.1007/s00223-019-00578-1. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Calcif Tissue Int. 2019. PMID: 31236621
-
Vitamin D supplementation in nursing home patients: randomized controlled trial of standard daily dose versus individualized loading dose regimen.Drugs Aging. 2015 May;32(5):371-8. doi: 10.1007/s40266-015-0259-8. Drugs Aging. 2015. PMID: 25899914 Clinical Trial.
-
Is calcifediol better than cholecalciferol for vitamin D supplementation?Osteoporos Int. 2018 Aug;29(8):1697-1711. doi: 10.1007/s00198-018-4520-y. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Osteoporos Int. 2018. PMID: 29713796 Review.
-
The Significance of Vitamin D in Adult Orthopaedics and Traumatology.Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2023 Oct 31;25(5):279-285. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0053.9676. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 38088102 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary Epigenetic Modulators: Unravelling the Still-Controversial Benefits of miRNAs in Nutrition and Disease.Nutrients. 2024 Jan 3;16(1):160. doi: 10.3390/nu16010160. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38201989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genetic and epigenetic contributions to the development of nutritional rickets.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 22;13:1059034. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1059034. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36619587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Diseases: From Physiology to Pathophysiology and Outcomes.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 30;12(4):768. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040768. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sumac-rose water mouthwash versus benzydamine to prevent radiation-induced oral mucositis in head and neck cancers: a phase II randomized trial.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Aug;149(10):7427-7439. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04687-1. Epub 2023 Mar 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36947237 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Olsen M.H., Angell S.Y., Asma S., Boutouyrie P., Burger D., A Chirinos J., Damasceno A., Delles C., Gimenez-Roqueplo A.-P., Hering D., et al. A call to action and a lifecourse strategy to address the global burden of raised blood pressure on current and future generations: The Lancet Commission on hypertension. Lancet. 2016;388:2665–2712. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31134-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

